systemd Network Manager TSN Endstation Configuration for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
Intel® ECI TSN Endstation introduces IEEE 802.1AS and IEEE 802.1Q-2018-EST (for example, Virtual LANs (VLANs), Earliest TxTime First (NET_SCHED_ETF) QDisc and Time Aware Priority (NET_SCHED_TAPRIO) QDisc) as systemd runtime services.
Intel® ECI makes generic assumptions that the Linux TSN Endstation settings are managed using ONLY distribution standard systemd Network Manager configurations rules for achieving IEEE 802.1Q-EST interoperability:
Attention
Intel® ECI maintains both feature backports and new Earliest TxTime First (NET_SCHED_ETF) QDisc and Time Aware Priority (NET_SCHED_TAPRIO) QDisc contribution for major Linux Debian* 11 (Bullseye) and Ubuntu* 22.04 (Jammy) mainlines, but all distribution support is on the way to upstream.
The following section is applicable to:

Setup the ECI APT repository, then run the following commands to install this component:
Install from individual Deb package
Install TSN Endstation boot services by
systemdtsn-endstation-initand dependencies:sudo apt install tsn-endstation-initFor example, on Debian 11 (Bullseye) distribution set with ECI Deb packages repository, the following should be displayed:
The following additional packages will be installed: ethtool network-irq-affinity The following NEW packages will be installed: ethtool network-irq-affinity tsn-endstation-init 0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 26 not upgraded. Need to get 188 kB/192 kB of archives. After this operation, 662 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Get:1 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 tsn-endstation-init all 3.0-bullseye-2 [3488 B] Get:2 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 isar/main amd64 ethtool amd64 1:5.9-1+igcfpe [182 kB] Get:3 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 isar/main amd64 network-irq-affinity all 1.1 [5984 B] Fetched 188 kB in 0s (7964 kB/s) debconf: delaying package configuration, since apt-utils is not installed Selecting previously unselected package ethtool. (Reading database ... 62295 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../ethtool_1%3a5.9-1+igcfpe_amd64.deb ... Unpacking ethtool (1:5.9-1+igcfpe) ... Selecting previously unselected package network-irq-affinity. Preparing to unpack .../network-irq-affinity_1.1_all.deb ... Unpacking network-irq-affinity (1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package tsn-endstation-init. Preparing to unpack .../tsn-endstation-init_3.0-bullseye-2_all.deb ... Unpacking tsn-endstation-init (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Setting up network-irq-affinity (1.1) ... Setting up ethtool (1:5.9-1+igcfpe) ... Setting up tsn-endstation-init (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ...Install TSN Endstation IEEE 802.1AS by
systemdtsn-endstation-timesyncruntime service:sudo apt install tsn-endstation-timesync iotg-gptp-configsFor example, on Debian 11 (Bullseye) distribution set with ECI Deb packages repository, the following should be displayed:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: linuxptp The following NEW packages will be installed: iotg-gptp-configs linuxptp tsn-endstation-timesync 0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 26 not upgraded. Need to get 181 kB/185 kB of archives. After this operation, 823 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Get:1 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 tsn-endstation-timesync all 3.0-bullseye-2 [4252 B] Get:2 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 linuxptp amd64 3.1 [177 kB] Get:3 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 iotg-gptp-configs amd64 0.8.27-bullseye-1.ae58048056 [3820 B] Fetched 181 kB in 0s (7568 kB/s) debconf: delaying package configuration, since apt-utils is not installed Selecting previously unselected package linuxptp. (Reading database ... 62196 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../linuxptp_3.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking linuxptp (3.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package iotg-gptp-configs. Preparing to unpack .../iotg-gptp-configs_0.8.27-bullseye-1.ae58048056_amd64.deb ... Unpacking iotg-gptp-configs (0.8.27-bullseye-1.ae58048056) ... Selecting previously unselected package tsn-endstation-timesync. Preparing to unpack .../tsn-endstation-timesync_3.0-bullseye-2_all.deb ... Unpacking tsn-endstation-timesync (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Setting up linuxptp (3.1) ... Setting up iotg-gptp-configs (0.8.27-bullseye-1.ae58048056) ... Setting up tsn-endstation-timesync (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ...Check the Intel ECI
systemdpackages upgrade with Earliest TxTime First (NET_SCHED_ETF) QDisc and Time Aware Priority (NET_SCHED_TAPRIO) QDisc features:sudo apt-cache policy systemdFor example, on Debian 11 (Bullseye) distribution set with ECI Deb packages repository, the following should be displayed:
root@eci-intel-3d56:~# systemd: Installed: 247.3-7 Candidate: 247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio Version table: 247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio 1000 1000 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye/dists/isar/InRelease isar/main amd64 Packages *** 247.3-7 500 500 http://lava.lavalab/mirrors/debian bullseye/main amd64 Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/statusInstall TSN Endstation IEEE 802.1Q-2018-EST runtime services
tsn-endstation-netlinkwithsystemdpackages upgrade, enabling the Earliest TxTime First (NET_SCHED_ETF) QDisc and Time Aware Priority (NET_SCHED_TAPRIO) QDisc built-in features:sudo apt install systemd tsn-endstation-netlinkFor example, on Debian 11 (Bullseye) distribution set with ECI Deb packages repository, the following should be displayed:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libpam-systemd libsystemd0 checkclocks Suggested packages: systemd-container Recommended packages: systemd-timesyncd | time-daemon The following NEW packages will be installed: tsn-endstation-netlink checkclocks The following packages will be upgraded: libpam-systemd libsystemd0 systemd 3 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 26 not upgraded. Need to get 5168 kB/5171 kB of archives. After this operation, 65.5 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Get:1 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 tsn-endstation-netlink all 3.0-bullseye-2 [3012 B] Get:2 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 libpam-systemd amd64 247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio [283 kB] Get:3 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 systemd amd64 247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio [4510 kB] Get:4 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 libsystemd0 amd64 247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio [376 kB] Get:5 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 checkclocks amd64 0.2 [14.2 kB] Fetched 5168 kB in 0s (58.7 MB/s) debconf: delaying package configuration, since apt-utils is not installed (Reading database ... 62337 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libpam-systemd_247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpam-systemd:amd64 (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) over (247.3-7) ... Preparing to unpack .../systemd_247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio_amd64.deb ... Unpacking systemd (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) over (247.3-7) ... Preparing to unpack .../libsystemd0_247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsystemd0:amd64 (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) over (247.3-7) ... Setting up libsystemd0:amd64 (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) ... Selecting previously unselected package tsn-endstation-netlink. (Reading database ... 62337 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../checkclocks_0.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking checkclocks (0.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package tsn-endstation-netlink. Preparing to unpack .../tsn-endstation-netlink_3.0-bullseye-2_all.deb ... Unpacking tsn-endstation-netlink (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Setting up checkclocks (0.2) ... Setting up systemd (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) ... Setting up libpam-systemd:amd64 (247.3-7-bullseye+etf+taprio) ... debconf: unable to initialize frontend: Dialog debconf: (No usable dialog-like program is installed, so the dialog based frontend cannot be used. at /usr/share/perl5/Debconf/FrontEnd/Dialog.pm line 78.) debconf: falling back to frontend: Readline Setting up tsn-endstation-netlink (3.0-bullseye-2) ... Processing triggers for dbus (1.12.20-2) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-13+deb11u3) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ...
eci-ethirqs@.service- Networking Interrupts CPU Affinity for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
Intel® Ethernet Controllers can provide several MSI interrupts to improve the network throughput.
Intel® ECI makes generic assumptions that traffic-class prioritization is achieved on cores (for example, real-time communication tasks) other than default core 0 (for example, house-keeping tasks) than Network Interrupts Affinity to CPU critical Ethernet device interrupts
This section describes how to selectively map MSI interrupts to particular CPU cores for each particular Intel® Ethernet Controller using systemctl.
The following section is applicable to:
Identify the available Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers:
$ lspci -nnn | grep "Ethernet controller"
The expected output will vary depending on the ODM:
00:1f.6 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation Ethernet Connection (2) I219-LM [8086:15b7] (rev 31) 01:00.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation Ethernet Controller I225-LM [8086:15f2] (rev 01) 02:00.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation I210 Gigabit Network Connection [8086:1533] (rev 03)
In this example, the output pattern is
${device_id} ${description}, where${device_id}is03:00.0.Important
Identify the Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controller interface that is wired to the TSN switch device or to another TSN end-station:
[Endpoint PCI
8086:7aacand8086:7aad] 12th Gen Intel® Core™ S-Series [Alder Lake] Ethernet GbE Time-Sensitive Network Controller[Endpoint PCI
8086:a0ac] 11th Gen Intel® Core™ U-Series and P-Series [Tiger Lake] Ethernet GbE Time-Sensitive Network Controller[Endpoint PCI
8086:4b32and8086:4ba0] Intel® Atom™ x6000 Series [Elkhart Lake] Ethernet GbE Time-Sensitive Network Controller[Endpoint PCI
8086:15f2] Intel® Ethernet Controller I225-LM for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)[Endpoint PCI
8086:157b,8086:1533,…] Intel® Ethernet Controller I210-T1 for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)
Confirm the Linux network interface name of the Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers:
$ networkctl status enp1s0
The expected output should be similar to the following, with the default
51-wired-dhcp.networkand99-default.linknetworkdand udev rules setting:root@eci-intel-23f0:~# networkctl status enp1s0 ? 5: enp1s0 Link File: /usr/lib/systemd/network/99-default.link Network File: /usr/lib/systemd/network/51-wired-dhcp.network Type: ether State: routable (configured) Path: pci-0000:01:00.0 Driver: igc Vendor: Intel Corporation Model: Ethernet Controller I225-LM HW Address: 00:a0:c9:00:00:00 (Intel Corporation) MTU: 1500 (min: 68, max: 9216) QDisc: mq IPv6 Address Generation Mode: eui64 Queue Length (Tx/Rx): 4/4 Auto negotiation: yes Speed: 1Gbps Duplex: full Port: tp Address: 10.10.10.19 (DHCP4 via 10.10.10.1) fe80::2a0:c9ff:fe00:0 Gateway: 10.10.10.1 (ALFA, INC.) DNS: 10.10.10.1 DHCP4 Client ID: IAID:0x56504d98/DUID DHCP6 Client DUID: DUID-EN/Vendor:0000ab11983c97c412262c820000 Connected To: cyclone5 on port 1c:a0:d3:20:06:1a (CE03) eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: Gained carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: DHCPv4 address 10.10.10.19/24 via 10.10.10.1 eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: Lost carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: DHCP lease lost eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: DHCPv6 lease lost eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: Gained carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: Lost carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: DHCPv6 lease lost eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: Gained carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[328]: enp1s0: DHCPv4 address 10.10.10.19/24 via 10.10.10.1
The output text is the interface name of i225 NIC, marked as
${interface_name}.Enable, start, and report the Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controller MSI interrupts affinity CPU cores for the particular Linux network interface name:
$ systemctl enable eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service ? /lib/systemd/system/eci-ethirqs@.service. ? eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service - ECI: set CPU core to IRQ Ethernet device affinity Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-ethirqs@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (exited) since Fri 2022-10-07 10:09:00 UTC; 4 years 1 months left Main PID: 23690 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Tasks: 0 (limit: 9164) Memory: 0B CPU: 0 CGroup: /system.slice/system-eci\x2dethirqs.slice/eci-ethirqs@enp1s0.service eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Starting ECI: set CPU core to IRQ Ethernet device affinity... eci-intel-23f0 network-irq-affinity[23690]: network-irq-affinity: Assigning enp1s0-TxRx-3 on IRQ 136 to CPU 1 eci-intel-23f0 network-irq-affinity[23690]: network-irq-affinity: Assigning enp1s0-TxRx-2 on IRQ 135 to CPU 1 eci-intel-23f0 network-irq-affinity[23690]: network-irq-affinity: Assigning enp1s0-TxRx-1 on IRQ 134 to CPU 1 eci-intel-23f0 network-irq-affinity[23690]: network-irq-affinity: Assigning enp1s0-TxRx-0 on IRQ 133 to CPU 0 eci-intel-23f0 network-irq-affinity[23690]: network-irq-affinity: Assigning enp1s0 on IRQ 132 to CPU 0 eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Finished ECI: set CPU core to IRQ Ethernet device affinity.
Confirm whether the interrupt mapping is effective:
$ cat /proc/interrupts | grep enp1s0
The expected output should be similar to the following:
root@eci-intel-3f6c:~# cat /proc/interrupts | grep enp3s0 CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3 132: 2508 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI 524288-edge enp1s0 133: 876072 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI 524289-edge enp1s0-TxRx-0 134: 165157 4380 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI 524290-edge enp1s0-TxRx-1 135: 165136 626 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI 524291-edge enp1s0-TxRx-2 136: 164913 617 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI 524292-edge enp1s0-TxRx-3
eci-ptp4l-p2p@.service - gPTP Time Synchronization Service for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
This section describes how to selectively enable IEEE 802.1as gPTP Profile Essential for each particular Intel® Ethernet Controller type using systemctl.
The following section is applicable to:
Set up Intel® Ethernet Controllers according to eci-ethirqs@.service- Networking Interrupts CPU Affinity for Intel® Ethernet Controllers.
Enable, start, and report the Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers IEEE 802.1AS on the particular Linux network interface name:
$ systemctl enable eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service ? /lib/systemd/system/eci-ptp4l-p2p@.service. ? eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service - ECI: Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service for enp1s0 Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-ptp4l-p2p@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-10-07 10:09:02 UTC; 4 years 1 months left Docs: man:ptp4l Main PID: 23783 (ptp4l) Tasks: 1 (limit: 9164) Memory: 572.0K CPU: 35ms CGroup: /system.slice/system-eci\x2dptp4l\x2dp2p.slice/eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service └─23783 ptp4l -f /run/eci/ptp4l-enp1s0.conf -i enp1s0 -ml 6 --step_threshold=1 --socket_priority=2 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: ptp4l[329420.035]: rms 4 max 6 freq +20886 +/- 2 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: [329420.035] rms 4 max 6 freq +20886 +/- 2 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: ptp4l[329421.037]: rms 2 max 4 freq +20888 +/- 3 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: [329421.037] rms 2 max 4 freq +20888 +/- 3 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: ptp4l[329422.040]: rms 2 max 3 freq +20887 +/- 3 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: [329422.040] rms 2 max 3 freq +20887 +/- 3 delay 12 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: ptp4l[329423.042]: rms 1 max 2 freq +20887 +/- 1 delay 13 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: [329423.042] rms 1 max 2 freq +20887 +/- 1 delay 13 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: ptp4l[329424.045]: rms 1 max 2 freq +20885 +/- 2 delay 13 +/- 0 eci-intel-23f0 ptp4l[23783]: [329424.045] rms 1 max 2 freq +20885 +/- 2 delay 13 +/- 0
Attention
You might need to edit Intel® Industrial Ethernet controllers IEEE 802.1AS to match a specific ODM Ethernet PHY configuration available on the the
iotg-gptp-configsECI package:$ ls -l /opt/intel/iotg_tsn_ref_sw/common/
Select a gPTP template from the list:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 526 Apr 21 2021 gPTP.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 540 Apr 21 2021 gPTP_RGMII-MV1510-1G.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 540 Apr 21 2021 gPTP_SGMII-MV2110-1G.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 543 Apr 21 2021 gPTP_SGMII-MV2110-2_5G.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 541 Apr 21 2021 gPTP_TI-1G.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 552 Apr 21 2021 gPTP_i225-1G.cfg
Edit gPTP settings required for certain Ethernet PHY and speed:
$ vi /run/eci/ptp4l-enp1s0.conf # # 802.1AS example configuration containing those attributes which # differ from the defaults. See the file, default.cfg, for the # complete list of available options. # [global] gmCapable 1 priority1 248 priority2 248 logAnnounceInterval 0 logSyncInterval -3 syncReceiptTimeout 3 neighborPropDelayThresh 800 min_neighbor_prop_delay -20000000 assume_two_step 1 path_trace_enabled 1 follow_up_info 1 transportSpecific 0x1 ptp_dst_mac 01:80:C2:00:00:0E network_transport L2 delay_mechanism P2P tx_timestamp_timeout 100 first_step_threshold 0.0
Then, restart to test and review gPTP settings:
$ systemctl restart eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service && journalctl -xe -u eci-ptp4l-p2p@enp1s0.service
eci-phc2sys@.service - PHC Time Synchronization Service for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
This section describes how to selectively enable IEEE 802.1as gPTP Profile Essential with CPU time on a particular Intel® Ethernet Controller type using systemctl.
The following section is applicable to:
Set up Intel® Ethernet controllers according to eci-ptp4l-p2p@.service - gPTP Time Synchronization Service for Intel® Ethernet Controllers.
Enable, start, and report the Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers’ PHC time sync on the particular Linux network interface name:
$ systemctl enable eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service → /lib/systemd/system/eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service. ? eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service - ECI: Synchronize system clock or PTP hardware clock (PHC) Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-phc2sys@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-10-07 10:09:02 UTC; 4 years 1 months left Docs: man:phc2sys Main PID: 23786 (phc2sys) Tasks: 1 (limit: 9164) Memory: 484.0K CPU: 48ms CGroup: /system.slice/system-eci\x2dphc2sys.slice/eci-phc2sys@enp1s0.service └─23786 phc2sys -s enp1s0 -c CLOCK_REALTIME --step_threshold=1 --transportSpecific=1 -w -ml 7 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: phc2sys[330852.178]: CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 2 s2 freq +17504 delay 1509 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: [330852.178] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 2 s2 freq +17504 delay 1509 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: phc2sys[330853.178]: CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 1 s2 freq +17503 delay 1509 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: [330853.178] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 1 s2 freq +17503 delay 1509 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: phc2sys[330854.178]: CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 4 s2 freq +17507 delay 1510 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: [330854.178] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 4 s2 freq +17507 delay 1510 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: phc2sys[330855.178]: CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 0 s2 freq +17504 delay 1507 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: [330855.178] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 0 s2 freq +17504 delay 1507 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: phc2sys[330856.178]: CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset -2 s2 freq +17502 delay 1512 eci-intel-23f0 phc2sys[23786]: [330856.178] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset -2 s2 freq +17502 delay 1512
eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@.service - TSN 802.1AS Services for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
This section describes how to selectively wait for IEEE 802.1as gPTP Profile Essential time synchronization on a particular Intel® Ethernet Controller using systemctl.
The following section is applicable to:
Set up Intel® Ethernet Controllers according to eci-phc2sys@.service - PHC Time Synchronization Service for Intel® Ethernet Controllers.
Enable, start, and wait for SUCCESS status of check_clocks for Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers on a particular Linux network interface name:
$ systemctl enable eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar after < 15 seconds to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service ? /lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@.service. ? eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service - ECI: Wait for clocks synchronization Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (exited) since Tue 2018-08-28 08:59:30 UTC; 27ms ago Process: 24138 ExecStart=/usr/bin/bash /usr/libexec/eci-tsn-wait-timesync.sh enp1s0 15 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 24138 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) CPU: 3ms eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: rt tstamp: 1535446769376683711 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: tai tstamp: 1535446806376683783 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: phc tstamp: 1535446806376685317 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: rt latency: 30 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: tai latency: 30 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: phc latency: 2080 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: phc-rt delta: 37000001606 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: phc-tai delta: 1534 eci-intel-23f0 bash[24139]: Clocks on this system are synchronized :) eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Finished ECI: Wait for clocks synchronization.
Optionally, enable, start, and monitor check_clocks for Intel® Industrial Ethernet Controllers on a particular Linux network interface name:
Important
gPTP monitoring and tracing is supported on certain Intel® Ethernet Controller supporting (PPS_CAPTUREASSERT callback pps_source_info API ):
[Endpoint PCI
8086:15f2] Intel® Ethernet Controller I225-LM for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)[Endpoint PCI
8086:157b,8086:1533,…] Intel® Ethernet Controller I210-T1 for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)
$ systemctl enable eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
? eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service - ECI: Check that time is synchronized Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (running) since Tue 2018-08-28 09:01:42 UTC; 22ms ago Main PID: 24159 (check_clocks) Tasks: 1 (limit: 9164) Memory: 284.0K CPU: 1ms CGroup: /system.slice/system-eci\x2dtsn\x2dtrack\x2dsync\x2d8021as.slice/eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service └─24159 check_clocks -d enp1s0 -va eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Starting ECI: Check that time is synchronized... eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Started ECI: Check that time is synchronized. eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: Dumping timestamps and deltas eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: /dev/pps0 can be enabled from /dev/ptp0 on device enp1s0 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: trying PPS source "/dev/pps0" eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: found PPS source "/dev/pps0" eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446903 sequence: 1928 offset: 3569 trt_lat=8184 tai_lat=37000008267 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446904 sequence: 1929 offset: 3688 trt_lat=4427 tai_lat=37000004486 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446905 sequence: 1930 offset: 4284 trt_lat=4721 tai_lat=37000004780 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446906 sequence: 1931 offset: 3651 trt_lat=4371 tai_lat=37000004415 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446907 sequence: 1932 offset: 4308 trt_lat=4446 tai_lat=37000004471 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446908 sequence: 1933 offset: 3663 trt_lat=4466 tai_lat=37000004493 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446909 sequence: 1934 offset: 3644 trt_lat=4313 tai_lat=37000004346 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446910 sequence: 1935 offset: 4233 trt_lat=4505 tai_lat=37000004555 eci-intel-23f0 check_clocks[24159]: pps-phc-timestamp: 1535446911 sequence: 1936 offset: 3662 trt_lat=4363 tai_lat=37000004397
For more logs:
$ journalctl -xe -u eci-tsn-track-sync-8021as@enp1s0.service | more
Report the check_clocks statistics to
ftracepulse-per-secondsequenceid-1075 to id-1084 interval for Intel® Industrial Ethernet controllers on the particular Linux network interface name:less /sys/kernel/tracing/per_cpu/cpu1/trace# tracer: nop # # entries-in-buffer/entries-written: 7/7 #P:4 # # _-------=> irqs-off # / _------=> need-resched # | / _-----=> need-resched-lazy # || / _----=> hardirq/softirq # ||| / _---=> preempt-depth # |||| / _--=> preempt-lazy-depth # ||||| / _-=> migrate-disable # |||||| / delay # TASK-PID CPU# ||||||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION # | | | ||||||| | | <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331549.637493: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447154.3793 seq=2179 tai_lat=37000004746 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331550.637510: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447155.3693 seq=2180 tai_lat=37000004506 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331568.637825: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447173.3772 seq=2198 tai_lat=37000004657 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331569.637842: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447174.3710 seq=2199 tai_lat=37000004450 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331570.637860: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447175.4131 seq=2200 tai_lat=37000004474 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331571.637877: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447176.3723 seq=2201 tai_lat=37000004374 ep=enp1s0 <...>-24159 [001] ....... 331572.637895: tracing_mark_write: 0: trace_event_clock_sync: parent_ts=1535447177.4119 seq=2202 tai_lat=37000004408 ep=enp1s0
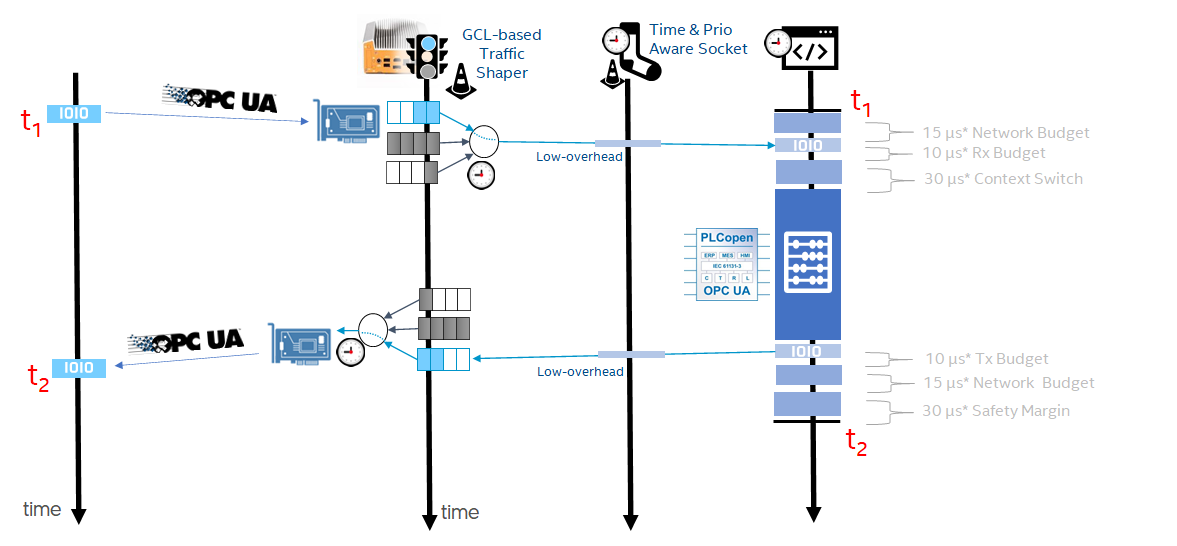
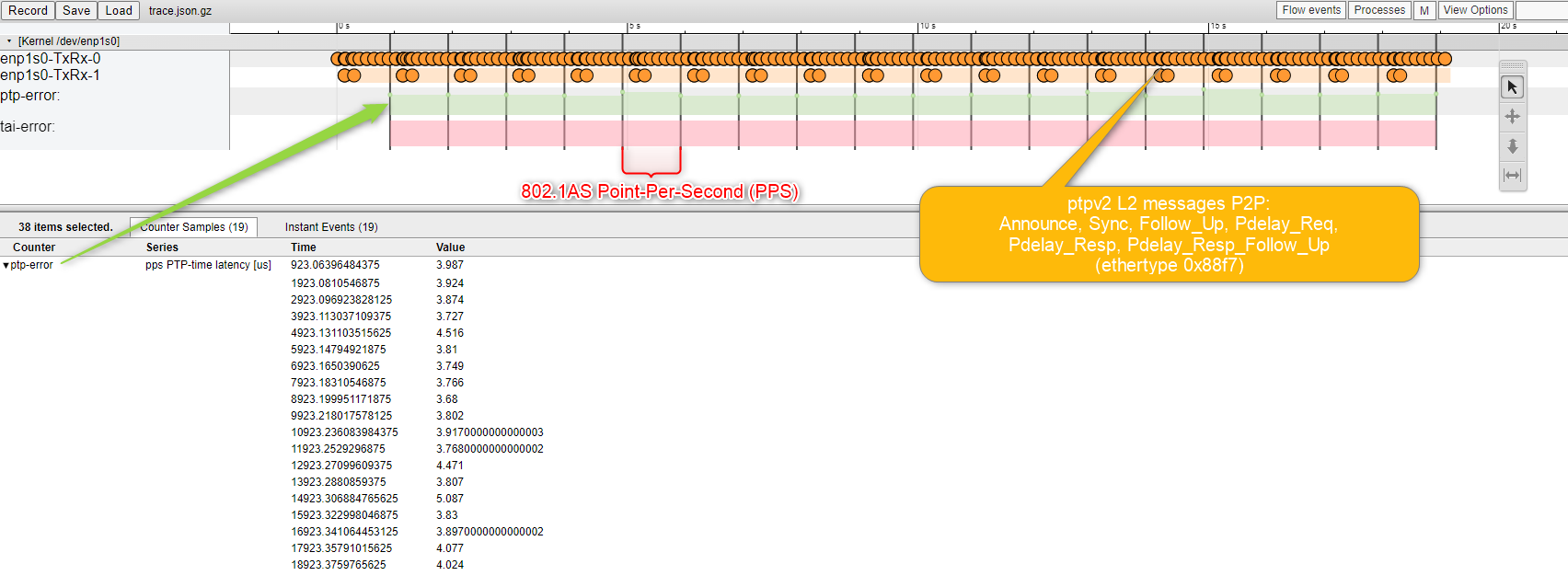
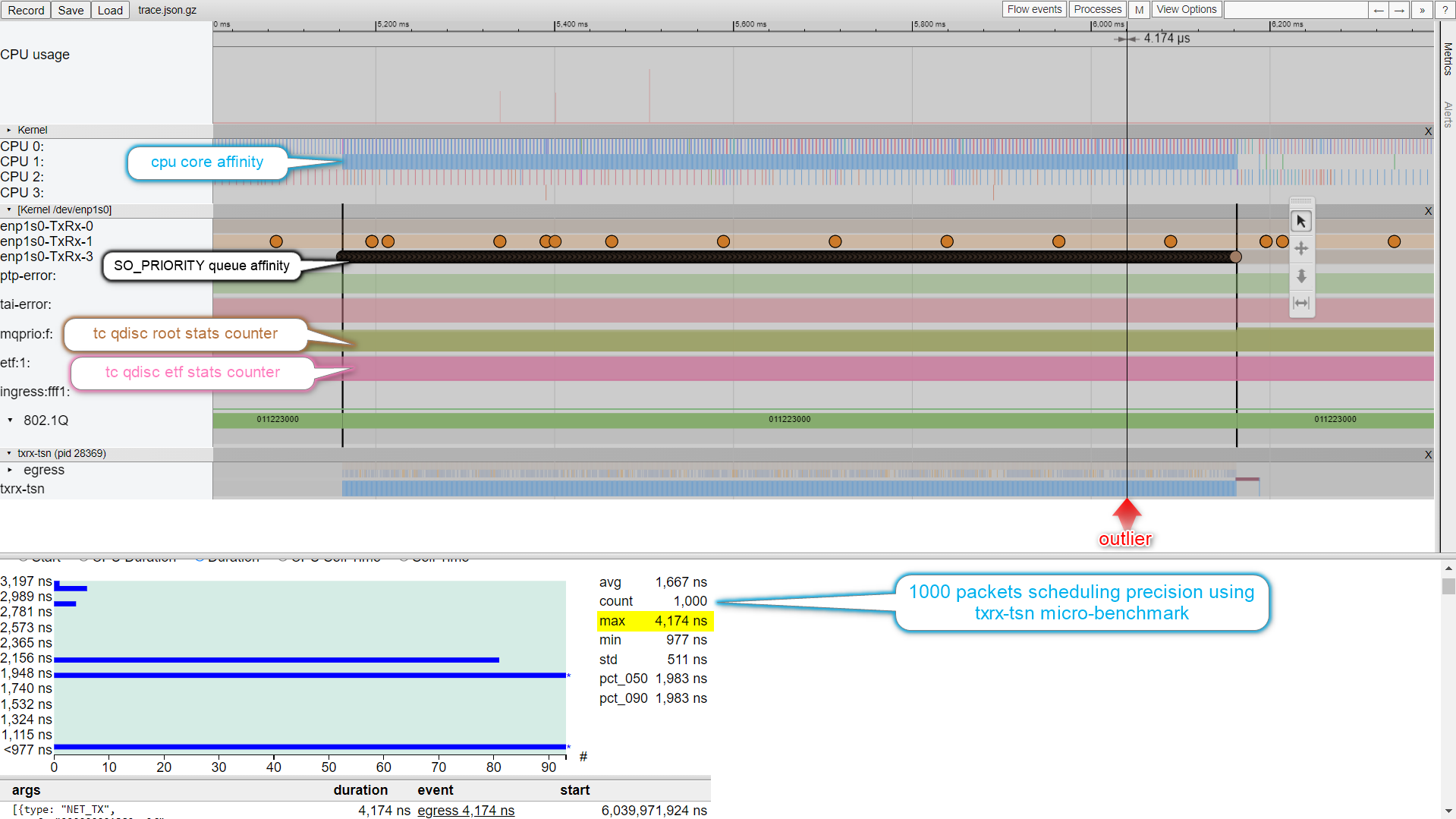
Visualize IEEE 802.1Q packet tracing in Timeview-UI for Intel® Industrial Ethernet controllers on the particular Linux network interface name:
Note:
To override International Atomic Time (TAI) and UTC
currentUtcOffsetdefault 37-second value:$ pmc -u -b 0 -t 1 \ "SET GRANDMASTER_SETTINGS_NP clockClass 248 clockAccuracy 0xfe offsetScaledLogVariance 0xffff currentUtcOffset 37 leap61 0 leap59 0 currentUtcOffsetValid 1 ptpTimescale 1 timeTraceable 1 frequencyTraceable 0 timeSource 0xa0"The expected output should be similar to the following:
sending: SET GRANDMASTER_SETTINGS_NP 2046a1.fffe.056bdc-0 seq 0 RESPONSE MANAGEMENT GRANDMASTER_SETTINGS_NP clockClass 248 clockAccuracy 0xfe offsetScaledLogVariance 0xffff currentUtcOffset 0 leap61 0 leap59 0 currentUtcOffsetValid 1 ptpTimescale 1 timeTraceable 1 frequencyTraceable 0 timeSource 0xa0
eci-tsn-netlink@.service - 802.1Q-2018 TSN Link-layer Service for Intel® Ethernet Controllers¶
It is strongly recommended to review systemd.network, systemd.link, and systemd.device unit files used for configuring a TSN Endstation.
$ man systemd.network
To familiarize with systemd supported Linux Traffic-Class features:
SYSTEMD.NETWORK(5) systemd.network SYSTEMD.NETWORK(5)
NAME
systemd.network - Network configuration
SYNOPSIS
network.network
DESCRIPTION
A plain ini-style text file that encodes network configuration for matching network interfaces, used by systemd-networkd(8). See systemd.syntax(7) for a general description
of the syntax.
The main network file must have the extension .network; other extensions are ignored. Networks are applied to links whenever the links appear.
The .network files are read from the files located in the system network directories /lib/systemd/network and /usr/local/lib/systemd/network, the volatile runtime network
directory /run/systemd/network and the local administration network directory /etc/systemd/network. All configuration files are collectively sorted and processed in lexical
order, regardless of the directories in which they live. However, files with identical filenames replace each other. Files in /etc/ have the highest priority, files in
/run/ take precedence over files with the same name under /usr/. This can be used to override a system-supplied configuration file with a local file if needed. As a special
case, an empty file (file size 0) or symlink with the same name pointing to /dev/null disables the configuration file entirely (it is "masked").
Along with the network file foo.network, a "drop-in" directory foo.network.d/ may exist. All files with the suffix ".conf" from this directory will be parsed after the file
itself is parsed. This is useful to alter or add configuration settings, without having to modify the main configuration file. Each drop-in file must have appropriate
section headers.
In addition to /etc/systemd/network, drop-in ".d" directories can be placed in /lib/systemd/network or /run/systemd/network directories. Drop-in files in /etc/ take
precedence over those in /run/ which in turn take precedence over those in /lib/. Drop-in files under any of these directories take precedence over the main network file
wherever located.
Note that an interface without any static IPv6 addresses configured, and neither DHCPv6 nor IPv6LL enabled, shall be considered to have no IPv6 support. IPv6 will be
automatically disabled for that interface by writing "1" to /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/ifname/disable_ipv6.
$ man systemd.link
To familiarize with systemd supported device configuration (for example, ethtool ioctl):
SYSTEMD.LINK(5) systemd.link SYSTEMD.LINK(5)
NAME
systemd.link - Network device configuration
SYNOPSIS
link.link
DESCRIPTION
A plain ini-style text file that encodes configuration for matching network devices, used by systemd-udevd(8) and in particular its net_setup_link builtin. See
systemd.syntax(7) for a general description of the syntax.
The link files are read from the files located in the system network directory /lib/systemd/network, the volatile runtime network directory /run/systemd/network, and the
local administration network directory /etc/systemd/network. Link files must have the extension .link; other extensions are ignored. All link files are collectively sorted
and processed in lexical order, regardless of the directories in which they live. However, files with identical filenames replace each other. Files in /etc/ have the
highest priority, files in /run/ take precedence over files with the same name in /lib/. This can be used to override a system-supplied link file with a local file if
needed. As a special case, an empty file (file size 0) or symlink with the same name pointing to /dev/null disables the configuration file entirely (it is "masked").
The link file contains a [Match] section, which determines if a given link file may be applied to a given device, as well as a [Link] section specifying how the device
should be configured. The first (in lexical order) of the link files that matches a given device is applied. Note that a default file 99-default.link is shipped by the
system. Any user-supplied .link should hence have a lexically earlier name to be considered at all.
See udevadm(8) for diagnosing problems with .link files.
Intel® ECI makes generic assumptions about the desired setting for several Intel® Ethernet Controllers capable to achieve IEEE 802.1Q-2018 network link configurations.
$ ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-netlink@.service.d/
The /usr/libexec/eci-tsn-netlink-nictype.sh helper script is used to instantiate unit files template on desired Linux network interface:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 798 Mar 5 2021 default-netif.link
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 606 Mar 5 2021 default-qos-mqprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Mar 5 2021 default-vlan.netdev
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1986 Mar 5 2021 i210-netif.link
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 717 Mar 5 2021 i210-qos-etf.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 607 Mar 5 2021 i210-qos-mqprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 942 Mar 5 2021 i210-qos-taprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Mar 5 2021 i210-vlan.netdev
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1710 Mar 5 2021 i225-netif.link
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 717 Mar 5 2021 i225-qos-etf.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 606 Mar 5 2021 i225-qos-mqprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 873 Mar 5 2021 i225-qos-taprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Mar 5 2021 i225-vlan.netdev
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1324 Mar 5 2021 mgbe-netif.link
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 734 Mar 5 2021 mgbe-qos-etf.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 622 Mar 5 2021 mgbe-qos-mqprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 930 Mar 5 2021 mgbe-qos-taprio.network
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Mar 5 2021 mgbe-vlan.netdev
This section describes how to enable IEEE 802.1Q-2018 Linux traffic control on a particular Intel® Ethernet controllers via systemd-networkd network manager.
The following section is applicable to:
Setup Intel® Ethernet controllers according to eci-tsn-wait-sync-8021as@.service - TSN 802.1AS Services for Intel® Ethernet Controllers.
Enable services to set 802.1Q-2018 basics or super-set 802.1Q-2018-EST link-layer configuration for Intel® Industrial Ethernet controllers on a particular Linux network interface name:
Important
Make sure that you have explored the Earliest TxTime First (NET_SCHED_ETF) QDisc usages.
$ systemctl enable eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service ? /lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@.service. ? eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service - ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Default Queue-Discipline preset Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (exited) since Tue 2018-08-28 12:28:51 UTC; 31ms ago Process: 24856 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/tc qdisc del root dev enp1s0 (code=exited, status=2) Process: 24857 ExecStart=/usr/libexec/eci-tsn-netlink-nictype.sh start enp1s0 etf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 24874 ExecStartPost=udevadm trigger /sys/class/net/enp1s0 --verbose --action=bind (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 24876 ExecStartPost=networkctl reload (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 24857 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) CPU: 31ms eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Starting ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Default Queue-Discipline preset... eci-intel-23f0 eci-tsn-netlink-nictype.sh[24857]: Setting up enp1s0 TSN Link QoS eci-intel-23f0 udevadm[24874]: /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0/net/enp1s0 eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Finished ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Default Queue-Discipline preset.
Verify whether the TSN Endstation systemd.network unit and systemd.link rules configuration files are set to the desired Linux network interface.
$ networkctl status enp1s0
The expected output should be similar to the following:
? 5: enp1s0 Link File: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link Network File: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.network Type: ether State: carrier (configured) Path: pci-0000:01:00.0 Driver: igc Vendor: Intel Corporation Model: Ethernet Controller I225-LM HW Address: 00:a0:c9:00:00:00 (Intel Corporation) MTU: 1500 (min: 68, max: 9216) QDisc: mqprio IPv6 Address Generation Mode: none Queue Length (Tx/Rx): 4/4 Auto negotiation: yes Speed: 1Gbps Duplex: full Port: tp
The
tsn-endstation-enp1s0.linkandtsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkin this example has mqprio ROOT QDisc assigned to the interface.Optionally, edit
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkudev rules for a desired interface with particular Intel Ethernet hardware offload capabilities:[Match] Name=enp1s0 [Network] #DHCP=no Description=The TSN-endstation physical ethernet device # Make netif member of VLAN interfaces on it: VLAN=enp1s0.vlan # In case of 'tagged only' setups, you probably don't need any IP # configuration on the link without VLAN (or: default VLAN). # For that just omit an [Address] section and disable all the # autoconfiguration magic like this: LinkLocalAddressing=no LLDP=no EmitLLDP=no IPv6AcceptRA=no IPv6SendRA=no [QDisc] Parent=ingress Handle=100 [MultiqueuePrioShaper] Parent=root Handle=1 Numtc=4 Priomap=0 1 1 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Queues=1@0 1@1 1@2 1@3 [EarliestTxTimeFirst] Parent=1:4 Handle=0 ClockId=CLOCK_TAI DeltaNSec=50000 Deadline=0 Offload=1 SkipSocket=0
Reapply
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkunit to enable all changes for the desired interface network interface:$ sudo systemctl restart eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@enp1s0.service $ tc qdisc show dev enp1s0 $ cat /proc/net/vlan/enp1s0.vlan
The
eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@.serviceexpected Linux Traffic Class output should be similar to the following:qdisc mqprio 1: root tc 4 map 0 1 1 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 queues:(0:0) (1:1) (2:2) (3:3) qdisc pfifo_fast 0: parent 1:3 bands 3 priomap 1 2 2 2 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 qdisc pfifo_fast 0: parent 1:2 bands 3 priomap 1 2 2 2 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 qdisc pfifo_fast 0: parent 1:1 bands 3 priomap 1 2 2 2 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 qdisc etf 8005: parent 1:4 clockid TAI delta 50000 offload on deadline_mode off skip_sock_check off qdisc ingress ffff: parent ffff:fff1 ---------------- enp1s0.vlan VID: 3 REORDER_HDR: 1 dev->priv_flags: 1021 total frames received 0 total bytes received 0 Broadcast/Multicast Rcvd 0 total frames transmitted 20 total bytes transmitted 3236 Device: enp1s0 INGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7 EGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7
The
eci-tsn-netlink-8021q@.serviceexpected hardware queues offload and Ethertype RX flow-type steering rules should be similar to the following:$ ethtool --show-features enp1s0 | grep -e hw-tc-offload -e ntuple-filters && ethtool -u enp1s0
ntuple-filters: on hw-tc-offload: on 4 RX rings available Total 4 rules Filter: 0 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x88F7 mask: 0x0 Action: Direct to queue 2 Filter: 1 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x0 mask: 0xFFFF VLAN EtherType: 0x0 mask: 0xffff VLAN: 0x2000 mask: 0x1fff User-defined: 0x0 mask: 0xffffffffffffffff Action: Direct to queue 1 Filter: 2 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x0 mask: 0xFFFF VLAN EtherType: 0x0 mask: 0xffff VLAN: 0x6000 mask: 0x1fff User-defined: 0x0 mask: 0xffffffffffffffff Action: Direct to queue 3
Important
Make sure that you have explored the Time Aware Priority (NET_SCHED_TAPRIO) QDisc usages.
$ systemctl enable eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service && systemctl start eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service && systemctl status eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service
The expected output should be similar to the following:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service ? /lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@.service. ? eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service - ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Enhanced-Scheduling Time (EST) Queue-Discipline preset Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: active (exited) since Wed 2018-08-29 07:32:45 UTC; 28ms ago Process: 25859 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/tc qdisc del root dev enp1s0 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 25866 ExecStart=/usr/libexec/eci-tsn-netlink-nictype.sh start enp1s0 taprio (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 25889 ExecStartPost=udevadm trigger /sys/class/net/enp1s0 --verbose --action=bind (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 25890 ExecStartPost=networkctl reload (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 25866 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) CPU: 30ms eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Starting ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Enhanced-Scheduling Time (EST) Queue-Discipline preset... eci-intel-23f0 eci-tsn-netlink-nictype.sh[25866]: Setting up enp1s0 TSN Link QoS eci-intel-23f0 udevadm[25889]: /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0/net/enp1s0 eci-intel-23f0 systemd[1]: Finished ECI: apply networkd 802.1Q Enhanced-Scheduling Time (EST) Queue-Discipline preset.
Verify whether the TSN end-station systemd.network unit and systemd.link rules configuration files are set to the desired Linux network interface.
$ networkctl status enp1s0
The expected output should be similar to the following:
? 5: enp1s0 Link File: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link Network File: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.network Type: ether State: carrier (configured) Path: pci-0000:01:00.0 Driver: igc Vendor: Intel Corporation Model: Ethernet Controller I225-LM HW Address: 00:a0:c9:00:00:00 (Intel Corporation) MTU: 1500 (min: 68, max: 9216) QDisc: taprio IPv6 Address Generation Mode: none Queue Length (Tx/Rx): 4/4 Auto negotiation: yes Speed: 1Gbps Duplex: full Port: tp
The
tsn-endstation-enp1s0.linkandtsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkin this example have mqprio ROOT QDisc assigned to the interface.Optionally, edit
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkudev rules for a desired interface with particular Intel Ethernet hardware offload capabilities:[Match] Name=enp1s0 [Network] #DHCP=no Description=The TSN-endstation physical ethernet device # Make netif member of VLAN interfaces on it: VLAN=enp1s0.vlan # In case of 'tagged only' setups, you probably don't need any IP # configuration on the link without VLAN (or: default VLAN). # For that just omit an [Address] section and disable all the # autoconfiguration magic like this: LinkLocalAddressing=no LLDP=no EmitLLDP=no IPv6AcceptRA=no IPv6SendRA=no [QDisc] Parent=ingress Handle=100 [TimeAwarePrioShaper] Parent=root Handle=1 Numtc=4 Priomap=0 1 1 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Queues=1@0 1@1 1@2 1@3 SchedEntry=S 01 500000 SchedEntry=S 0e 500000 # MY Begining-of-Time is Wednesday 29 August 2018 07:40:00 Basetime=1535528400000000000 # I225-LM required past-time paradise .e.g. no reCalibration BasetimeCalibration=0 #No GuardCycles= Cycletime=1000000 CycletimeExtension=0 TxTimeMode=hwoffload TxTimeDelay=0
Reapply
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.networkunit to enable all changes for the desired interface network interface:$ sudo systemctl restart eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@enp1s0.service $ tc qdisc show dev enp1s0 $ cat /proc/net/vlan/enp1s0.vlan
The
eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@.serviceexpected Linux Traffic Class output should be similar to the following:qdisc taprio 1: root refcnt 5 tc 4 map 0 1 1 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 queues offset 0 count 1 offset 1 count 1 offset 2 count 1 offset 3 count 1 clockid invalid flags 0x2 base-time 1535528400000000000 cycle-time 1000000 cycle-time-extension 0 index 0 cmd S gatemask 0x1 interval 500000 index 1 cmd S gatemask 0xe interval 500000 qdisc pfifo 0: parent 1:4 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 1:3 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 1:2 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 1:1 limit 1000p qdisc ingress ffff: parent ffff:fff1 ---------------- enp1s0.vlan VID: 3 REORDER_HDR: 1 dev->priv_flags: 1021 total frames received 0 total bytes received 0 Broadcast/Multicast Rcvd 0 total frames transmitted 20 total bytes transmitted 3236 Device: enp1s0 INGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7 EGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7
The
eci-tsn-netlink-8021q-est@.serviceexpected hardware queues offload and Ethertype RX flow-type steering rules should be similar to the following:$ ethtool --show-features enp1s0 | grep -e hw-tc-offload -e ntuple-filters && ethtool -u enp1s0
ntuple-filters: on hw-tc-offload: on 4 RX rings available Total 4 rules Filter: 0 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x88F7 mask: 0x0 Action: Direct to queue 1 Filter: 1 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x0 mask: 0xFFFF VLAN EtherType: 0x0 mask: 0xffff VLAN: 0x2000 mask: 0x1fff User-defined: 0x0 mask: 0xffffffffffffffff Action: Direct to queue 3 Filter: 2 Flow Type: Raw Ethernet Src MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Dest MAC addr: 00:00:00:00:00:00 mask: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Ethertype: 0x0 mask: 0xFFFF VLAN EtherType: 0x0 mask: 0xffff VLAN: 0x6000 mask: 0x1fff User-defined: 0x0 mask: 0xffffffffffffffff Action: Direct to queue 3
Note:
Restarting only
systemd-networkd.servicewill NOT be sufficient to override priorsystemdunit files :Clear traffic-class prior QDisc
tc qdisc root del dev enp1s0is required.Triggering udev bind action
tc qdisc root del dev enp1s0is required.Clear
vlanip link del enp1s0.vlanis required.
Optionally, edit
/run/systemd/network/enp1s0.vlan.netdevdevice unit configuration for TSN Endstation VLAN ingress and egress QoS (for example, VLAN ID and PCP):[NetDev] Name=enp1s0.vlan Kind=vlan [VLAN] Description=The TSN-endstation VLAN RT-traffic class ethernet device Id=3 EgressQOSMaps=1-1 2-2 3-3 4-4 5-5 6-6 7-7 IngressQOSMaps=1-1 2-2 3-3 4-4 5-5 6-6 7-7
Note: Restarting
systemd-networkd.servicewill NOT override existingsystemd.deviceunit configurations. You need to clean prior VLAN configurations.$ ip link del enp1s0.vlan $ sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd $ cat /proc/net/vlan/enp1s0.vlan
The expected output should be similar to the following:
enp1s0.vlan VID: 3 REORDER_HDR: 1 dev->priv_flags: 1021 total frames received 0 total bytes received 0 Broadcast/Multicast Rcvd 0 total frames transmitted 20 total bytes transmitted 3236 Device: enp1s0 INGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7 EGRESS priority mappings: 0:0 1:1 2:2 3:3 4:4 5:5 6:6 7:7
Optionally, edit
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.linkudev rules for a desired interface with particular Intel Ethernet hardware offload capabilities:[Match] Driver=igc OriginalName=enp1s0 [Link] NamePolicy=kernel database onboard path slot AlternativeNamesPolicy=database onboard path slot MACAddressPolicy=persistent # Unset I225-LM default hw-offload ReceiveVLANCTAGHardwareAcceleration=0 TransmitVLANCTAGHardwareAcceleration=0 ReceiveVLANCTAGFilter=0 TransmitVLANSTAGHardwareAcceleration=0 TCPSegmentationOffload=0 GenericSegmentationOffload=0 GenericReceiveOffload=0 # Disable I225-LM Energy-Efficient Ethernet EeeEnable=0 # Set I225-LM Flow control RxFlowControl=1 TxFlowControl=1 AutoNegotiationFlowControl=1 # Enable I225-LM RX Hw-Filters # PTPv2 message -> Queue1 # Vlan PCP 1-2 -> Queue2 # Vlan PCP 3-4 -> Queue3 NTupleFilter=1 NfcFlowType=ether proto 0x88f7 queue 1 NfcFlowType=ether vlan 0x2000 m 0x1FFF queue 3 NfcFlowType=ether vlan 0x6000 m 0x1FFF queue 3 # Enable I225-LM 802.1QBV & 802.1QBU hw-offload HwTcOffload=1 FramePreemption=1 # Enable I225-LM all 4 queues CombinedChannels=4 # Optional I225-LM parameters #RxCoalesceSec= #RxMaxCoalescedFrames= #RxCoalesceIrqSec= #RxMaxCoalescedIrqFrames= #TxCoalesceSec= #TxMaxCoalescedFrames= #TxCoalesceIrqSec= #TxMaxCoalescedIrqFrames= #StatisticsBlockCoalesceSec= #UseAdaptiveRxCoalesce= #UseAdaptiveTxCoalesce= #CoalescePacketRateLow= #RxCoalesceLowSec= #RxMaxCoalescedLowFrames= #TxCoalesceLowSec= #TxMaxCoalescedLowFrames= #CoalescePacketRateHigh= #RxCoalesceHighSec= #RxMaxCoalescedHighFrames= #TxCoalesceHighSec= #TxMaxCoalescedHighFrames= #CoalescePacketRateSampleIntervalSec= #RxBufferSize=256 #TxBufferSize=256
Reapply
/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.linkudev rules to enable all changes for the desired interface network interface:$ sudo udevadm trigger /sys/class/net/enp1s0 --verbose --action=bind && journalctl -b -u systemd-udevd
The expected output with
systemd-udevd.serviceDEBUG level message should be similar to the following:eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: Config file /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link is applied eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: autonegotiation is unset or enabled, the speed and duplex are not writable. eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-generic-segmentation eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-gro eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-tcp-segmentation eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-ntuple-filter eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : l2-fwd-offload eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : hw-tc-offload eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-vlan-hw-insert eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-vlan-hw-parse eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-vlan-filter eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-vlan-stag-hw-insert eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: netlink: set user frame-preemption eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: rtnl: received non-static neighbor, ignoring. eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: enp1s0: Flags change: -LOWER_UP -RUNNING eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: Sent message type=signal sender=n/a destination=n/a path=/org/freedesktop/network1/link/_35 interface=org.freedesktop.DBus.Prop> eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: enp1s0: Lost carrier eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: enp1s0: State is failed, dropping config eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: netlink: set user eee eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: clear nfc rx rules 4/64: Success eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: netlink: user set nfc rx rules needed=4 eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x0] rule : Success eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x1] rule : Success eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x2] rule : Success eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x3] rule : Success eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: Device has addr_assign_type=0 eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: MAC on the device already matches policy *persistent* eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: Device has name_assign_type=4 eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: Policy *path* yields "enp1s0". eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/80-net-setup-link.rules:11 NAME 'enp1s0' eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25516]: enp1s0: sd-device: Created db file '/run/udev/data/n5' for '/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0/net/enp1s0'
Visualize IEEE 802.1Q packet tracing in Timeview-UI for Intel® Industrial Ethernet controllers on the particular Linux network interface name:
TSN Endstation Troubleshooting¶
How do I activate systemd-networkd.service, systemd-udevd.service, or both DEBUG log-level messages?**
The `systemd-udevd.service` udev rules tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link parsed errors or driver limitations need debugging. Activate systemd-udevd.service DEBUG log-level message using the drop-in file with the following content:
$ mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/systemd-udevd.service.d/
$ vi /etc/systemd/system/systemd-udevd.service.d/10-debug.conf
[Service]
Environment=SYSTEMD_LOG_LEVEL=debug
Then, apply the same approach for debugging systemd-networkd.service unit file tsn-endstation-enp1s0.network parse errors and driver limitations. Activate systemd-networkd.service DEBUG log-level message using the drop-in file with the following content:
$ mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/systemd-networkd.service.d
$ vi /etc/systemd/system/systemd-networkd.service.d/10-debug.conf
[Service]
Environment=SYSTEMD_LOG_LEVEL=debug
Reload and restart systemd-networkd.service and systemd-udevd.service to apply the drop-in files :
$ systemctl daemon-reload
$ systemctl restart systemd-udevd && systemctl restart systemd-networkd
Visualize the debug info, warnings, and errors :
$ journalctl -b -u systemd-udevd -u systemd-networkd
...
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule space-separation split argp[2]=0xA000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule space-separation split argp[3]=m
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule space-separation split argp[4]=0x1FFF
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule space-separation split argp[5]=queue
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule space-separation split argp[6]=3
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule parser start : ether vlan 0xA000 m 0x1FFF queue 3
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: Found 'ether' 7 options of flow-type RX rules
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: Matched 'vlan' RX rule value argp[2]=0xA000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: Matched 'vlan-mask' RX rule mask argp[4]=0x1FFF
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: Matched 'queue' RX rule value argp[6]=3
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link:32: nfc: flow-type RX rule parser Succeed : ether vlan 0xA000 m 0x1FFF queue 3
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[25470]: Parsed configuration file /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: enp1s0.vlan: NDisc handler get timeout event
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[25466]: enp1s0.vlan: link_check_ready(): DHCP4 or DHCP6 is enabled but no dynamic address is assigned yet.
...
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: Config file /run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.link is applied
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: autonegotiation is unset or enabled, the speed and duplex are not writable.
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-generic-segmentation
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-gro
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-tcp-segmentation
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-ntuple-filter
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : l2-fwd-offload
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : hw-tc-offload
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-vlan-hw-insert
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-vlan-hw-parse
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : rx-vlan-filter
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set feature bit : tx-vlan-stag-hw-insert
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: netlink: set user frame-preemption
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: netlink: set user eee
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: clear nfc rx rules 4/64: Success
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: netlink: user set nfc rx rules needed=4
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x0] rule : Success
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x1] rule : Success
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x2] rule : Success
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: ethtool: set rx nfc flow-type [id=0x3] rule : Success
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: Device has addr_assign_type=0
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: MAC on the device already matches policy *persistent*
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: Device has name_assign_type=4
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: Policy *path* yields "enp1s0".
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/80-net-setup-link.rules:11 NAME 'enp1s0'
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: sd-device: Created db file '/run/udev/data/n5' for '/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0/net/enp>
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: Device (SEQNUM=4178, ACTION=bind) processed
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-udevd[26303]: enp1s0: sd-device-monitor: Passed 813 byte to netlink monitor
...
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: found matching network '/run/systemd/network/00-tsn-endstation-enp1s0.network'
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_FLAGS: 2
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_SCHED_CYCLE_TIME: 1000000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_SCHED_CYCLE_TIME_EXTENSION: 0
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: Orig: 1535528400000000000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: Now : 1535531048107213912
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: Specified 'basetime' as expired! No Recalibration
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_SCHED_BASE_TIME: 1535528400000000000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY index: 0
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_SCHED_ENTRY_CMD: 0
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY_GATE_MASK: 1
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY_INTERVAL: 500000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY index: 1
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_ATTR_SCHED_ENTRY_CMD: 0
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY_GATE_MASK: e
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: TCA_TAPRIO_SCHED_ENTRY_INTERVAL: 500000
eci-intel-23f0 systemd-networkd[26408]: enp1s0: Configuring traffic control
...
How do I stress test 802.1Q-2018 link layer?
Install the TSN Endstation test helper services provided by the tsn-endstation-loadtest package.
sudo apt install tsn-endstation-loadtest
For example, on Debian 11 (Bullseye) distribution set with ECI Deb packages repository, the following should be displayed:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
iperf3 xdpdump
The following NEW packages will be installed:
iperf3 tsn-endstation-loadtest xdpdump
0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 26 not upgraded.
Need to get 38.4 kB/40.1 kB of archives.
After this operation, 120 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
Get:1 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 tsn-endstation-loadtest all 3.0-bullseye-2 [1736 B]
Get:2 http://lava.lavalab/mirrors/debian bullseye/main amd64 iperf3 amd64 3.9-1 [28.4 kB]
Get:3 http://lava.lavalab/wheeljack/apt-repos/ECI/3.0/bullseye/eci-bullseye isar/main amd64 xdpdump amd64 1.1-bullseye [9976 B]
Fetched 38.4 kB in 0s (132 kB/s)
debconf: delaying package configuration, since apt-utils is not installed
Selecting previously unselected package iperf3.
(Reading database ... 62263 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../iperf3_3.9-1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking iperf3 (3.9-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package xdpdump.
Preparing to unpack .../xdpdump_1.1-bullseye_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking xdpdump (1.1-bullseye) ...
Selecting previously unselected package tsn-endstation-loadtest.
Preparing to unpack .../tsn-endstation-loadtest_3.0-bullseye-2_all.deb ...
Unpacking tsn-endstation-loadtest (3.0-bullseye-2) ...
Setting up xdpdump (1.1-bullseye) ...
Setting up iperf3 (3.9-1) ...
Setting up tsn-endstation-loadtest (3.0-bullseye-2) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ...