Complete and Verify Deployment¶
The section is applicable to:

Do the following to complete and verify ECI deployment:
Reboot the target system, if not already done. When the system boots to the GRUB menu, there should be a menu entry for ECI at the top of the GRUB menu list. Select this menu entry, or wait five seconds for this menu entry to automatically boot.
Note: Ubuntu* hides the GRUB menu by default, so you may not see it without first enabling it.
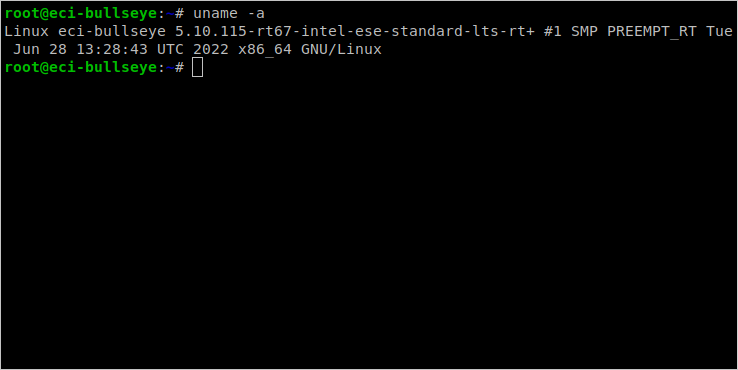
Login to the system and verify that the ECI Linux* Intel LTS PREEMPT_RT kernel is active by running the command
uname -a. The output of this command should contain the following based on which kernel was installed:Linux Intel LTS PREEMPT_RT kernel:
...-intel-ese-standard-lts-rt+ #1 SMP PREEMPT_RT ...Linux Intel LTS Xenomai Dovetail kernel:
...-intel-ese-standard-lts-dovetail+ #1 SMP PREEMPT ...
Install ECI Deb Packages from APT Repository¶
At this point, you should be able to install most ECI Deb packages using the APT package manager on this target system. For a complete list of available ECI Deb packages, refer to ECI Packages Lists.
The following figure illustrations some of meta-packages (high-level Deb packages) available:
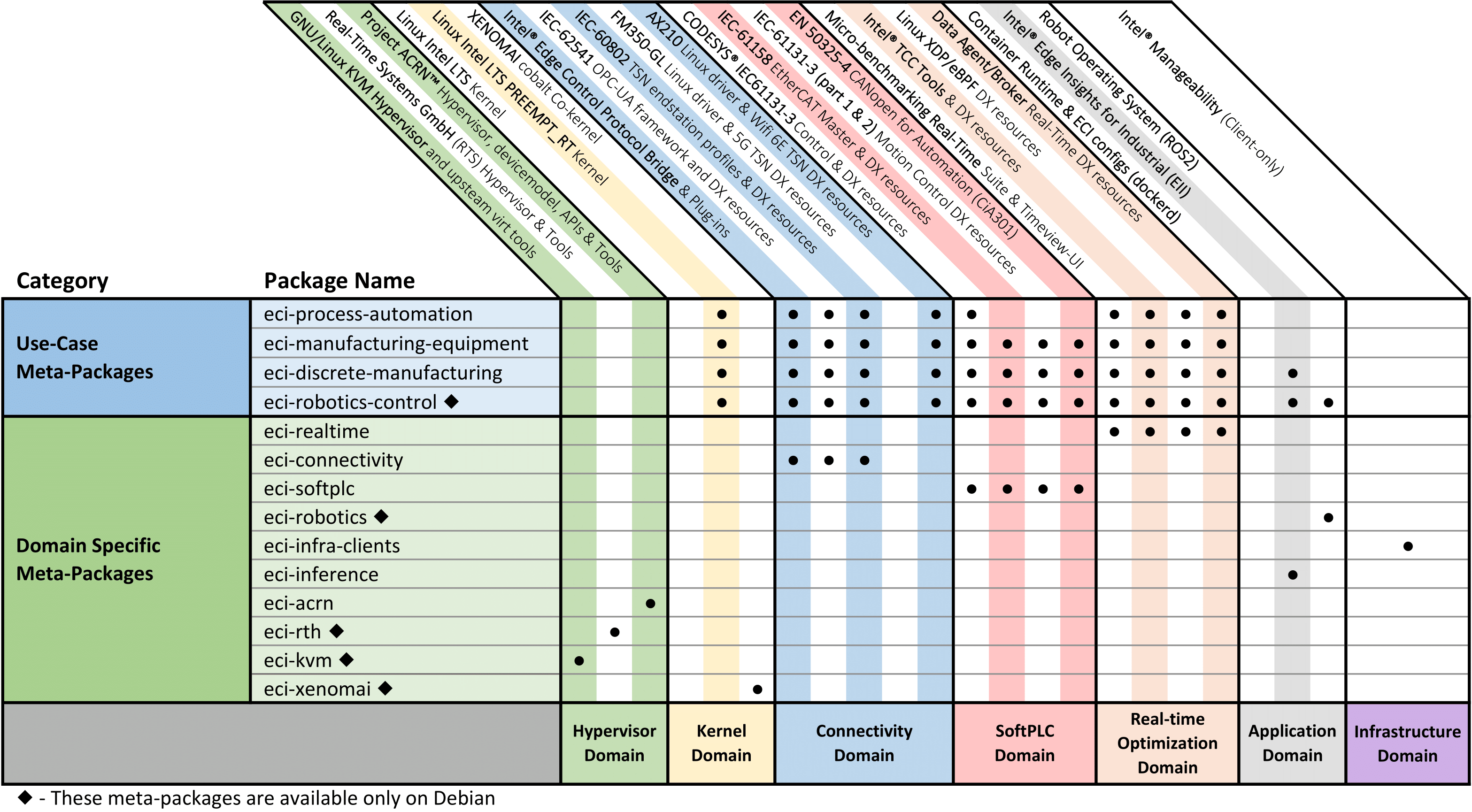
Here are some meta-packages that you could start with:
Meta-package |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Includes real-time optimization domain packages, such as benchmarks and Intel® Time Coordinated Computing. |
|
Includes connectivity domain packages for Time Sensitive Networking and industrial fieldbuses, such as Intel® Edge Control Protocol Bridge, IEC-62541 OPC-UA framework, and IEC-60802 TSN. |
|
Includes software PLC domain packages, such as CODESYS® IEC61131-3, IEC-61158 EtherCAT Master, IEC-61131-3 (part 1 & 2) Motion Control, and IEC-50325-4 CANopen. |
For example, to install the eci-realtime meta-package, perform the following command:
$ sudo apt install eci-realtime
If you are installing any robotics related packages such as eci-robotics or eci-robotics-control, set up the Intel oneAPI and ROS2 APT repositories:
# download the key to system keyring $ sudo wget -O- https://apt.repos.intel.com/intel-gpg-keys/GPG-PUB-KEY-INTEL-SW-PRODUCTS.PUB | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/oneapi-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null # add signed entry to apt sources and configure the APT client to use Intel repository: $ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/oneapi-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.repos.intel.com/oneapi all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/oneAPI.list # download the key to system keyring $ sudo wget -O- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.key | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/ros-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null # add signed entry to apt sources and configure the APT client to use ROS repository: $ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/ros-archive-keyring.gpg] http://packages.ros.org/ros2/ubuntu $(source /etc/os-release && echo $VERSION_CODENAME) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros2.list $ sudo apt updateAttention
If you are located in the People’s Republic of China, modify the
/etc/hostsfile to directly connect to the raw.githubusercontent server:$ sudo bash -c "echo '185.199.108.133 raw.githubusercontent.com' >> /etc/hosts"
Where to go Next?¶
(Recommended) Run a benchmark, such as Caterpillar, which helps to evaluate the benefits of cache allocation on a real-time OS.
For more information on the various components ECI has to offer, refer to Components and Features of ECI.
For more information on developing real-time applications using ECI, refer to Developer Resources.
Visit the Edge Controls for Industrial online support forum for questions and answers.