RTH GPOS and POS Test Concurrent Workloads¶
This section assumes that your target is already running RTS with access to the Privileged OS (POS) and (General Purpose OS (GPSO). Otherwise, refer to RTH Prerequisites and Real-Time Systems Hypervisor (RTH).
Furthermore, this section will use Debian* GNU/Linux* 11 (bullseye) for both operating systems.
The idea of this section is to run a real-time (RT) workload (or benchmark) on the POS, while running a non real-time (RT) workload (or noise) on the GPOS:
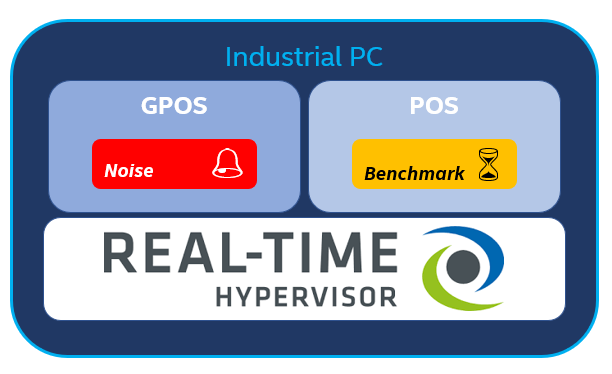
Basically, you can use any benchmark in /opt/benchmarking/ for testing the system. For the details of individual benchmarks, refer to Benchmarks & Performance Characterization. However, for this section a CODESYS Software PLC application,
namely CODESYS Benchmarking Applications can be used. Also, for generating noise, stress-ng will be used.
Additionally, this section will use SSH connections to POS and GPOS via a single Ethernet device.
Either follow Sanity Check #1: Communication between Virtualized and Privileged OS Runtimes or use the systemd service approach to establish a SSH connection to GPOS:
Create the following service:
`vim /etc/systemd/system/pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service:[Unit] Description=Forward SSH port from POS to GPOS After=systemd-networkd.service [Service] ExecStart=/etc/systemd/network/pos-forward.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
#. Next, find the MAC-Address of your SSH Ethernet device using either the ifconfig or the ip a command. That is, match your
IP address and the network interface device, providing the right MAC-Address. For example, look for ether 00:e0:4c:3e:f2:19 if
using `ifconfig`:
enx00e04c3ef219: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.44.52 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.44.255 inet6 fe80::2e0:4cff:fe3e:f219 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:e0:4c:3e:f2:19 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 27543 bytes 5054966 (4.8 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 15490 bytes 1442772 (1.3 MiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Now, create the script calling
iptables, as triggered by thesystemdservice:vim /etc/systemd/network/pos-forward.sh:#!/bin/bash OS=`uname -r` GPOS="intel-pk-standard" MAC="00:e0:4c:3e:f2:19" INTF="" # empty string BRIDGE="" # empty string sleep 5 # give some time to get ready for the BRIDGE if [ -n "$MAC" ]; then if [[ $OS == *"$GPOS"* ]]; then BRIDGE=$(ip a | grep -B2 "inet 192.168.2.1" | awk -F'[ :]+' '$1 && $1!="lo" {print $2}') if [ -n "$BRIDGE" ] then echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/$BRIDGE/forwarding else echo "Not able to detect BRIDGE for ip-forwarding!" exit 1 fi INTF=$(ip a | grep -B1 "$MAC" | awk -F'[ :]+' '$1 && $1!="lo" {print $2}') if [ -n "$INTF" ] then echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/$INTF/forwarding # flush iptables -F iptables -t nat -F # port forwarding iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p tcp --dport 2222 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:22 # CODESYS iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p udp --dport 1740 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:1740 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p udp --dport 1741 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:1741 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p udp --dport 1742 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:1742 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p udp --dport 1743 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:1743 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p tcp --dport 11740 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:11740 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p tcp --dport 1217 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:1217 iptables -A PREROUTING -t nat -i $INTF -p tcp --dport 1217 -j DNAT --to 192.168.2.2:4840 # accept forwarded packets iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 2222 -j ACCEPT # CODESYS iptables -A FORWARD -p udp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 1740 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p udp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 1741 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p udp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 1742 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p udp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 1743 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 11740 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 1217 -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -d 192.168.2.2 --dport 4840 -j ACCEPT # masquerade iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING ! -s 127.0.0.1 -j MASQUERADE iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $INTF -j MASQUERADE iptables -L else echo "Not able to get MAC from cmdline for INTF!" exit 1 fi fi fi
Note: Make sure to use your
MAC="..."address in the script.Finally, make the script executable
chmod +x /etc/systemd/network/pos-forward.shby starting thesystemdservice:systemctl start pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service && systemctl status pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service
Wait for a couple of seconds and check the status:
● pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service - Forward SSH port from POS to GPOS Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d └─10-override-protect-proc.conf Active: inactive (dead) since Thu 2021-09-09 18:00:11 UTC; 1h 25min ago Process: 813 ExecStart=/etc/systemd/network/pos-forward.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 813 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: target prot opt source destination Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: Chain DOCKER (0 references) Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: target prot opt source destination Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 (0 references) Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: target prot opt source destination Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 (0 references) Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: target prot opt source destination Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: Chain DOCKER-USER (0 references) Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 pos-forward.sh[844]: target prot opt source destination Sep 09 18:00:11 eci-intel-07e7 systemd[1]: pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service: Succeeded. # (optional) enable the service to start automatically after a reboot systemctl enable pos_to_gpos_ipforward.service
Now, you should be able to SSH to the POS and GPOS from the same IP address.
Here is an example from the GPOS terminal:
$ ssh root@192.168.44.52
Here is an example from the POS terminal:
$ ssh root@192.168.44.52 -p 2222
For POS, the standard SSH port 22 is redirected to the GPOS port 2222.
The target benchmark (or RT workload) is CODESYS ST-Fragment. Please get the main details
about this benchmark from the provided link. For any other details on CODESYS, refer to CODESYS Software PLC.
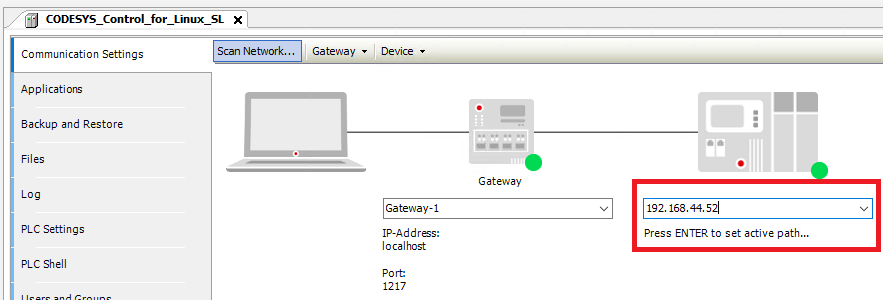
However, note that in this best-known-method, the CODESYS related ports used to communicate with the IDE (download the application to the target)
are as well ‘port forwarded’ from POS to GPOS (refer to the pos-forward.sh script). Using the regular Scan Network... might not work.
Instead, enter the target IP address directly:
If you are not able to connect, restart the CODESYS service:
$ systemctl restart codesyscontrol.service
Now, continue with Download (Execute) Directly to Target. Once the application is downloaded and started,
SSH to the POS ssh root@192.168.44.52 -p 2222 and check the generated results in the file under /var/opt/codesys/PlcLogic/.
Now, create some noise on the GPOS. SSH to the GPOS ssh root@192.168.44.52. Using stress-ng, noise (or non-RT workload) is simulated.
For example, put some load on the GPOS CPUs using the stress-ng --cpu 2 command. Now, if returning to the POS, restart the ST-Fragment benchmark
by restarting the CODESYS service: systemctl restart codesyscontrol.service. This will capture a RT workload results file, while a non-RT workload
(stress-ng) is running on the GPOS:
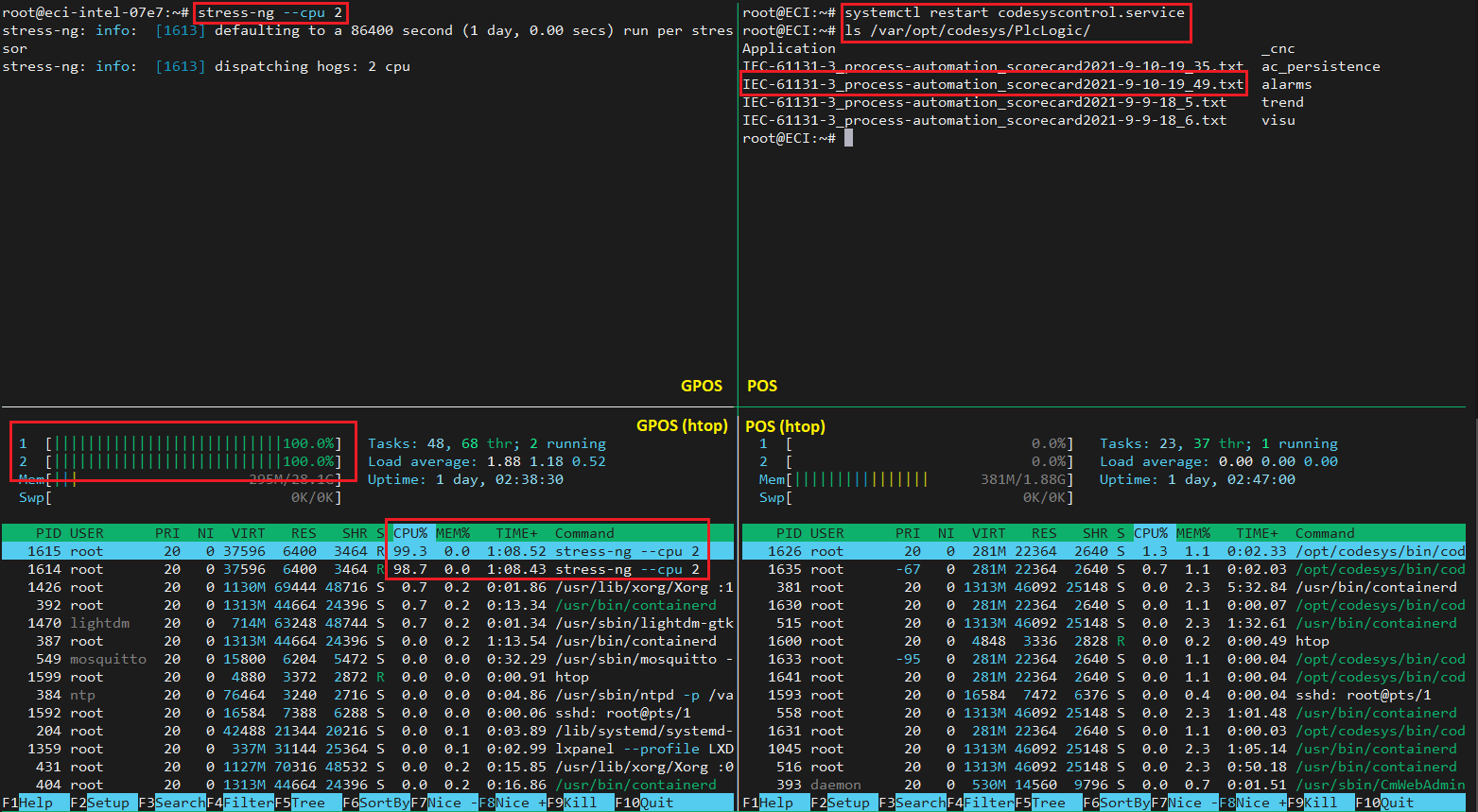
On the left hand side of the image (GPOS), stress-ng is executed on the top, whereas monitoring is done via htop on the bottom.
On the right hand side of the image (POS), CODESYS service is restarted to trigger a new benchmark file (top), while also monitoring on the bottom.
Now, compare both results files. Obviously, one file should be captured without any ‘noise’ first, while the second file is running stress-ng.
Ideally, the values should not differ significantly as the noise running on the GPOS should be isolated from the POS via the hypervisor.
For instance, counter-checking by running stress-ng --cpu 2 on POS and restarting the CODESYS service to generate a new
result file, should show significant differences.
Another way of creating some non-RT workload (or noise) is to run some graphics stress. Here it is recommended to connect directly to the
screen output and use a monitor to access the desktop. Then, run a terminal and execute glxheads or another glx
workload:
You may also install any other workload using apt install, if your GPOS is Debian* GNU/Linux* 11 (Bullseye).