CODESYS Benchmark¶
The CODESYS benchmark is an example application that allows deterministic control and test of the CODESYS SoftPLC. The application is defined such that a main task occurs every 250us. Within the main task is a configurable workload which iterates a number of user defined times. The specific workload is configurable to either: “floating point”, “arithmetic”, or “boolean” operations. Cycle execution times are measured from which minimum, maximum, and jitter measurements are derived. These measurements allow performance characterization of the CODESYS SoftPLC on the target system.
This benchmark can be ran natively, or in a container environment. Running in a container environment is easier to setup, but will perform slightly worse than running natively. If you’re running this benchmark for the first time, it is recommended to run in a container environment.
Setup the ECI repository, if not done already.
Install the CODESYS ECI Benchmark PLC logic and convenience scripts from the ECI repository:
 $ sudo apt install codesys-eci-benchmark codesys-benchmark-scripts
$ sudo apt install codesys-eci-benchmark codesys-benchmark-scripts
$ sudo dnf install codesys-eci-benchmark codesys-benchmark-scriptsUse the provided scripts to start the CODESYS Linux runtime. The scripts will perform various optimizations to minimize interrupts to the CODESYS Linux runtime. When the CODESYS Linux runtime starts, it will auto-load and execute the OPC UA Client Benchmark prebuilt PLC logic.
$ sudo /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility/start_codesys_native.shThe scripts available at
/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utilityinclude:
start_codesys_native.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below), stops non-essential services, and restarts the CODESYS Linux runtime
start_codesys_container.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below) and starts the containerized CODESYS Linux runtime with RT priority
taskset_codesys.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below)The provided scripts also perform the following runtime optimizations:
Uses Cache Allocation Technology (CAT) to allocate exclusive access of half the last-level cache to isolated cores (typically 1 & 3)
Assigns CODESYS task affinity to isolated cores (typically 1 & 3)
Assigns non-CODESYS task affinity to core 0
Disables kernel machine check interrupt
Increases thread runtime utilization to infinity
When executing the scripts, not all task affinity can be changed. This is expected behavior. An example output is shown below:
$ sudo /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility/start_codesys_native.sh Stopping unecessary services Failed to stop ofono.service: Unit ofono.service not loaded. Failed to stop wpa_supplicant.service: Unit wpa_supplicant.service not loaded. Failed to stop bluetooth.service: Unit bluetooth.service not loaded. Stopping Docker Daemon Warning: Stopping docker.service, but it can still be activated by: docker.socket Stopping Codesys Runtime Disabling Machine Check Disabling RT runtime limit New COS default: 0xff0 Changing CPU affinity of existing interrupts setting 1 to affine for core 0 setting 4 to affine for core 0 setting 8 to affine for core 0 setting 9 to affine for core 0 setting 12 to affine for core 0 setting 14 to affine for core 0 setting 16 to affine for core 0 setting 18 to affine for core 0 setting 27 to affine for core 0 setting 29 to affine for core 0 setting 120 to affine for core 0 setting 121 to affine for core 0 setting 123 to affine for core 0 setting 124 to affine for core 0 setting 125 to affine for core 0 setting 126 to affine for core 0 taskset: failed to set pid 3's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 4's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 16's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 23's affinity: Invalid argument Starting Codesys Runtime Changing affinity of Codesys Runtime tasks Codesys preparation complete.Verify that CODESYS Linux runtime started correctly:
$ sudo systemctl status codesyscontrolThe output should show
Active: active (running):$ sudo systemctl status codesyscontrol ● codesyscontrol.service - LSB: Prepares and starts codesyscontrol Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/codesyscontrol; generated) Active: active (running) since Fri 2023-03-03 19:59:10 MST; 1s ago Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8) Process: 121981 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/codesyscontrol start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Tasks: 2 (limit: 14185) Memory: 13.0M CGroup: /system.slice/codesyscontrol.service └─121986 /opt/codesys/bin/codesyscontrol.bin /etc/CODESYSControl.cfg Mar 03 19:59:09 eci-test systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Prepares and starts codesyscontrol... Mar 03 19:59:10 eci-test codesyscontrol[121981]: codesyscontrol started Mar 03 19:59:10 eci-test systemd[1]: Started LSB: Prepares and starts codesyscontrol.The CODESYS benchmark is configured to host a web visualization at
http://<target-ip-address>:8080. Open this URL in a web browser. If the benchmark is working correctly, the web visualization should be similar to the following image:Tip
If you cannot connect to the web server, verify that port 8080 is not blocked by a firewall. On Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® based systems, you may need to open port 8080 in the firewall with the following commands:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload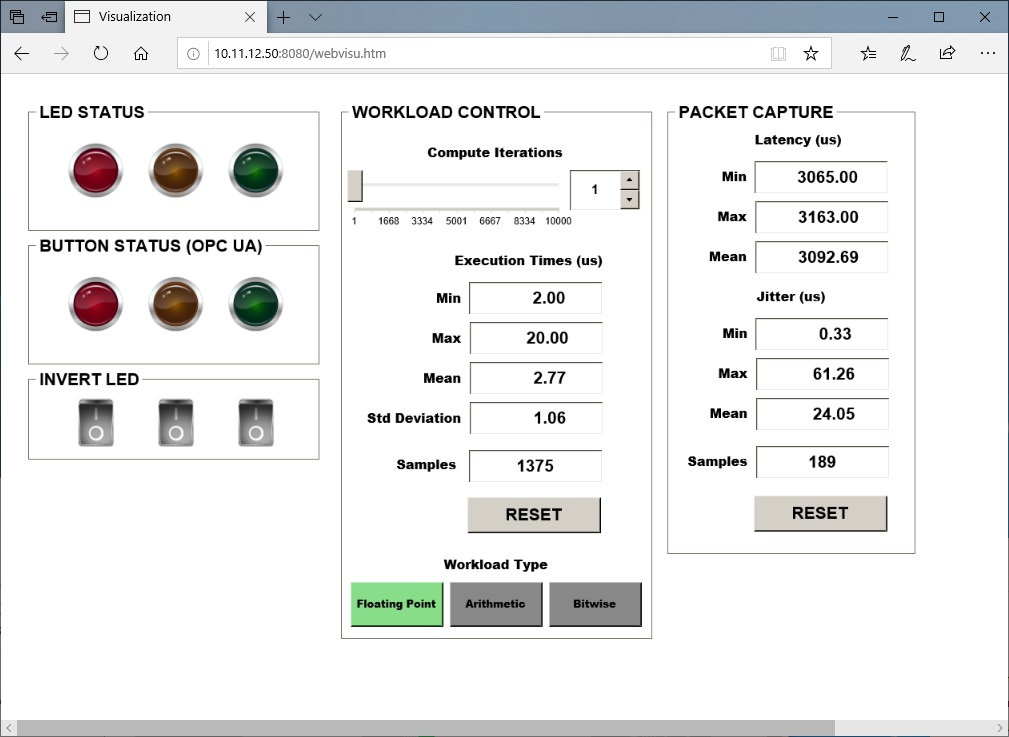
Run the
taskset_codesys.shscript at/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utilityto move all CODESYS tasks to isolated CPU cores (1,3 or 2,4) and change the priority of all CODESYS tasks to RT:$ ./taskset_codesys.shUse the RESET buttons in the web visualization to reset the statistics after running the
taskset_codesys.shscript. This CODESYS benchmark demonstrates that real-time performance can be achieved with proper kernel and runtime configurations.Use the slider and arrow buttons to increase or decrease the number of workload iterations per cycle.
The colored LEDs are connected to variables mapped to an OPC UA server. Connect an OPC UA client to the CODESYS OPC UA server to read/write the values. You can download a popular free OPC UA client called UaExpert from: https://www.unified-automation.com/products/development-tools/uaexpert.html.
The following steps are applicable to:

Install a container engine, if not already done:

The preferred container engine on Debian and Canonical® Ubuntu® based systems is Docker. Install Docker on the target system, if not already done.
The preferred container engine on Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® based systems is Podman. Install Podman on the target system, if not already done:
$ sudo dnf install podmanOn the target system, install the
codesys-benchmark-scriptspackage from the ECI repository. Setup the ECI repository, then perform the following command to install this component:
 $ sudo apt install codesys-benchmark-scripts
$ sudo apt install codesys-benchmark-scripts
$ sudo dnf install codesys-benchmark-scriptsNavigate to
/opt/benchmarking/codesysand build thecodesyscontrolcontainer image with thecodesys-eci-benchmarkbenchmark:
 $ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/docker $ docker build -f ./Dockerfile.controlruntime \ -t codesyscontrol:4.5.0.0 . \ --build-arg ECI_DEB=codesys-eci-benchmark \ --build-arg CDS_VERSION=4.5.0.0
$ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/docker $ docker build -f ./Dockerfile.controlruntime \ -t codesyscontrol:4.5.0.0 . \ --build-arg ECI_DEB=codesys-eci-benchmark \ --build-arg CDS_VERSION=4.5.0.0
$ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/docker $ sudo podman build --format docker \ -f ./Dockerfile.controlruntime \ -t codesyscontrol:4.5.0.0 . \ --build-arg ECI_DEB=codesys-eci-benchmark \ --build-arg CDS_VERSION=4.5.0.0Note
If you are building behind a proxy, you may need to add the following build arguments:
--build-arg http_proxy="http://<proxy:port>" --build-arg https_proxy="http://<proxy:port>".Navigate to
/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility. This directory contains a number of useful scripts for improving the real-time performance of the CODESYS Linux runtime.The scripts available at
/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utilityinclude:
start_codesys_native.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below), stops non-essential services, and restarts the CODESYS Linux runtime
start_codesys_container.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below) and starts the containerized CODESYS Linux runtime with RT priority.
taskset_codesys.sh: Optimizes the system (see list below)The provided scripts also perform the following runtime optimizations:
Uses Cache Allocation Technology (CAT) to allocate exclusive access of half the last-level cache to isolated cores (typically 1 & 3)
Assigns CODESYS task affinity to isolated cores (typically 1 & 3)
Assigns non-CODESYS task affinity to core 0
Disables kernel machine check interrupt
Increases thread runtime utilization to infinity
When executing the scripts, not all task affinity can be changed. This is expected behavior. An example output is shown below:
$ sudo /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility/start_codesys_native.sh Stopping unecessary services Failed to stop ofono.service: Unit ofono.service not loaded. Failed to stop wpa_supplicant.service: Unit wpa_supplicant.service not loaded. Failed to stop bluetooth.service: Unit bluetooth.service not loaded. Stopping Docker Daemon Warning: Stopping docker.service, but it can still be activated by: docker.socket Stopping Codesys Runtime Disabling Machine Check Disabling RT runtime limit New COS default: 0xff0 Changing CPU affinity of existing interrupts setting 1 to affine for core 0 setting 4 to affine for core 0 setting 8 to affine for core 0 setting 9 to affine for core 0 setting 12 to affine for core 0 setting 14 to affine for core 0 setting 16 to affine for core 0 setting 18 to affine for core 0 setting 27 to affine for core 0 setting 29 to affine for core 0 setting 120 to affine for core 0 setting 121 to affine for core 0 setting 123 to affine for core 0 setting 124 to affine for core 0 setting 125 to affine for core 0 setting 126 to affine for core 0 taskset: failed to set pid 3's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 4's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 16's affinity: Invalid argument taskset: failed to set pid 23's affinity: Invalid argument Starting Codesys Runtime Changing affinity of Codesys Runtime tasks Codesys preparation complete.Run the
start_codesys_container.shscript available at/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utilityto reload the CODESYS Linux runtime and start the benchmark:
 $ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility $ sudo ./start_codesys_container.sh
$ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility $ sudo ./start_codesys_container.sh
$ cd /opt/benchmarking/codesys/utility $ sudo ./start_codesys_container.sh podmanThe CODESYS benchmark is configured to host a web visualization at
http://<target-ip-address>:8080. Open this URL in a web browser. If the benchmark is working correctly, the web visualization should be similar to the following image:Tip
If you cannot connect to the web server, verify that port 8080 is not blocked by a firewall. On Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® based systems, you may need to open port 8080 in the firewall with the following commands:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Run the
taskset_codesys.shscript at/opt/benchmarking/codesys/utilityto move all CODESYS tasks to isolated CPU cores (1,3 or 2,4) and change the priority of all CODESYS tasks to RT:$ sudo ./taskset_codesys.shUse the RESET buttons in the web visualization to reset the statistics after running the
taskset_codesys.shscript. This CODESYS benchmark demonstrates that real-time performance can be achieved with proper kernel and runtime configurations.Use the slider and arrow buttons to increase or decrease the number of workload iterations per cycle.
The colored LEDs are connected to variables mapped to an OPC UA server. Connect an OPC UA client to the CODESYS OPC UA server to read/write the values. You can download a popular free OPC UA client called UaExpert from: https://www.unified-automation.com/products/development-tools/uaexpert.html.

