systemd Intel® Ethernet TSN Endpoint boot and runtime services¶
Linux systemd services is often used by OT network administrators to re-configure automatically a network interface on any ECI nodes :
/lib/systemd/system/tsn_bootconf.serviceallows root user to enforce on a selected <IFACE> (ex: enp1s0) TSN essential parameters at service startup through kernel command-line (ie. dynamic IP address, static IP address, virtual LAN (VLAN), and queueing discipline) without need for Linux rootfs persistence. This method is particularly interesting with ECI-R (RTS Hypervisor) privileged-RTOS rootfs images mounted as RAM disk.Tip
To modify the kernel command-line parameters, edit the configuration file located at:
/boot/EFI/BOOT/grub.cfg. Append the parameters to the line that begins withlinux /bzImage. If Thetsnep=command-line parameter is omitted, the tsn_bootconf.service fallback onto first detected Intel I210 NIC and use it as default TSN endpoint.Service startup command:
$ cat /proc/cmdline BOOT_IMAGE=/bzImage root=PARTUUID=704dc9f2-3fa5-4161-9774-f3b3fbea15f3 rw rootwait tsnep=192.168.0.10/255.255.255.0,enp1s0 qdisc=TAPRIO_ETF tsn.vlan=3 quiet console=ttyS0,115200 console=tty0 clocksource=tsc tsc=reliable nmi_watchdog=0 nosoftlockup noht audit=0 irqaffinity=0 isolcpus=1-3 rcu_nocbs=1-3 nohz_full=1-3 intel_pstate=disable intel.max_cstate=0 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 processor.max_cstate=0 processor_idle.max_cstate=0 $ systemctl enable tsn_bootconf $ systemctl start tsn_bootconf
Service teardown command:
$ systemctl stop tsn_runconf $ systemctl disable tsn_runconf
/lib/systemd/system/tsn_runconf@.serviceallows root user to enforce on a selected <IFACE> (ex: enp1s0) TSN essential parameters at service startup through/etc/tsninit-networkd.conffile (ie. dynamic IP address, static IP address, virtual LAN (VLAN), and queueing discipline).Service startup command:
$ vi /etc/tsninit-networkd.conf tsn.vlan=5 qdisc=TAPRIO_ETF tsnep=192.168.0.10/255.255.255.0, $ systemctl enable tsn_runconf@enp1s0 $ systemctl start tsn_runconf@enp1s0
Note
no CR character at the end of
/etc/tsninit-networkd.conffile for theenp1s0string to append to the command argument.Service teardown command :
$ systemctl stop tsn_runconf@enp1s0 $ systemctl disable tsn_runconf@enp1s0
Custom netlink-tsninit script¶
The /usr/libexec/netlink-tsninit script start|stop individual underlying systemd services :
ethtool@<IFACE>.servicewith ETHTOOL_ARGS argument variable under/etc/ethtool.confptp4l@<IFACE>.servicewith OPTIONS argument variable under/etc/ptp4l.confphc2sys@<IFACE>.servicewith OPTIONS_PH2SYS and OPTIONS_PMC= argument variables under/etc/phc2sys.conf
Configure the [interface] to get IP Address dynamically from DHCP server¶
Note
DHCP mode is the default behavior. If the tsnenp parameter is omitted, DHCP will be used by default.
tsnep=dhcp,[interface]Example - Configure the interface
enp6s0to get an IP address dynamically from DHCP server:tsnep=dhcp,enp6s0
Configure the [interface] with a static [ip address] with [netmask]¶
tsnep=[ip address]/[netmask],[interface]Example - Configure the interface
enp6s0with static IP address10.11.12.50and netmask of255.255.255.0:tsnep=10.11.12.50/255.255.255.0,enp6s0
Create a Virtual LAN (VLAN) with [vlan id] on the [interface]¶
The
tsn.vlanparameter is optional. Omitting this parameter will cause no VLAN to be configured.tsn.vlan=[vlan id]Example - Create a VLAN with ID of 100 on interface:
tsn.vlan=100
Configure Queueing Discipline (Qdisc) rule used on the [interface]¶
The
qdiscparameter is optional. Omitting this parameter will cause no Queue Discipline to be configured.Tip
MQPRIO - Priority to traffic class mapping shaper
The MQPRIO qdisc is a simple queuing discipline that allows mapping traffic flows to hardware queue ranges using priorities and a configurable priority to traffic class mapping. A traffic class in this context is a set of contiguous qdisc classes which map 1:1 to a set of hardware exposed queues.
To modify the configuration used by MQPRIO, see section: Configure Priority into Traffic Class Table
Tip
TAPRIO - Time-aware traffic shaper
The TAPRIO qdisc implements a simplified version of the scheduling state machine defined by IEEE 802.1Q-2018 Section 8.6.9, which allows configuration of a sequence of gate states, where each gate state allows outgoing traffic for a subset (potentially empty) of traffic classes.
To modify the configuration used by TAPRIO, see section: Configure Gate Control List (GCL)
Tip
TAPRIO_ETF - Qdisc TAPRIO IEEE 802.1Q-2018 EST-shaper with socket-based
SCM_TXTIMEand ETF-offloadTip
TAPRIO_TA - Qdisc TAPRIO IEEE 802.1Q-2018 EST-shaper in TxTime-assisted mode
Tip
TAPRIO_OL - Qdisc TAPRIO IEEE 802.1Q-2018 EST-shaper in TxTime-offload mode
qdisc=[MQPRIO/TAPRIO/TAPRIO_ETF/TAPRIO_TA/TAPRIO_OL]Example - Enable Queue Discipline on interface with TAPRIO rule selected:
qdisc=TAPRIO
Configure Priority into Traffic Class Table¶
Tip
Follow this section to modify the configuration used by Queue Discipline when MQPRIO rule is selected.
The configuration is created as a file located at: /usr/lib/systemd/user/queue-s1.cfg.
Each line is record-oriented and requires the following format:
PRIORITY QUEUE [ETF] [DELTA]
PRIORITY, the column of priority configuration.
QUEUE, the column of traffic class (also named queue) configuration.
ETF, the column of Time-aware traffic shaper configuration. The value can be a space, ‘etf’ or ‘etf_deadline’.
DELTA, the column of a configurable time until which before packets transmission time, ETF buffers packets.
A sample configuration is shown as below:
# PRIORITY QUEUE [ETF] [DELTA] 5 0 etf 5000000 3 1 etf 5000000 7 2
Configure Gate Control List (GCL)¶
Tip
Follow this section to modify the configuration used by Queue Discipline when TAPRIO rule is selected.
The configuration is created as a file located at: /usr/lib/systemd/user/gates-s4.sched.
Each line is record-oriented and requires the following format:
S [GATE STATE] [DURATION]
GATE STATE, The gate state value is a numerical representation of the intended gate-state. Octal (prefixed 0), decimal, and hexadecimal (prefixed 0x) notation is allowed. The gate of traffic class N is set at bit position N. The gate is open if the corresponding bit is set to 1 and closed if set to 0.
DURATION, the duration of gate being opened.
A sample configuration is shown as below:
S 08 100000 S 01 100000 S 02 100000 S 04 200000 S 08 100000 S 01 100000 S 02 100000 S 04 200000
Builtin systemd-networkd.service [Experimental]¶
Linux systemd-stable (master) has introduces builtin Linux Traffic-control Qdisc configuration from standard /lib/systemd/network/*.network configurations rules.
ECI previews the systemd-networkd Traffic-control builtin TAPRIO and ETF Qdisc support (v244.3-backport) and provide configuration placeholder for OT administrators aiming to experiment alternative IEEE 802.1Q-2018 EST TSN traffic-shaper setup at OS runtime.
$ find /etc/systemd/network -name *netif.link
/etc/systemd/network/11-i210-netif.link
/etc/systemd/network/10-tgl-mgbe-netif.link
/etc/systemd/network/12-i225-netif.link
$ vi /etc/systemd/network/11-i210-netif.link
[Match]
Driver=igb
[Link]
NamePolicy=path
# [TrafficControlQueueingDiscipline]
# Parent=0
# TimeAwarePrioShaperNumtc=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperPriomap=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperQueues=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperSchedEntry=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperBasetime=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperCycletime=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperCycletimeExtension=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperTxTimeMode=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperTxTimeDelay=
# TimeAwarePrioShaperClockid=
# [TrafficControlQueueingDiscipline]
# Parent=100
# EarliestTxTimeFirstClockid=CLOCK_TAI
# EarliestTxTimeFirstDelta=500
# EarliestTxTimeFirstDeadline=N
# EarliestTxTimeFirstOffload=Y
# EarliestTxTimeFirstSkipsock=Y
# [TrafficControlQueueingDiscipline]
# Parent=100
# EarliestTxTimeFirstClockid=CLOCK_TAI
# EarliestTxTimeFirstDelta=500
# EarliestTxTimeFirstDeadline=N
# EarliestTxTimeFirstOffload=Y
# EarliestTxTimeFirstSkipsock=Y
Important
The following patch series applies from ECI Yocto ROOTFS build recipes meta-intel-tsn/recipes-core/systemd/systemd_%.bbappend on top of Yocto Dunfell-stable systemd v244.3 (commit-id c4280c342bbf4fa8da833103482362236c18f835) :
Add Misc. v245 tc shaper addition and netlink support backported to v244.3 stable.
0001-sd-netlink-support-NLMSGERR_ATTR_MSG.patch
0002-network-include-NLMSGERR_ATTR_MSG-attribute-in-error.patch
0003-sd-netlink-add-support-for-ifb-device.patch
0004-networkd-tc-introduce-tbf.patch
0005-network-ignore-sections-which-have-both-NetworkEmula.patch
0006-network-rename-QDiscs-to-QDisc.patch
0007-network-make-network_emulator_fill_message-take-Netw.patch
0008-network-drop-unnecessary-headers.patch
0009-network-tc-introduce-sfq-Stochastic-Fairness-Queuein.patch
0010-network-SFQ-cannot-be-configured-with-netem-or-TBF.patch
0011-network-tc-add-more-options-for-TBF.patch
0012-network-tc-qdisc-parent-add-support-to-set-ingress.patch
0013-sd-netlink-make-TCA_OPTIONS-take-NETLINK_TYPE_UNION.patch
0014-network-tc-Add-support-to-conkfigure-CoDel-Controlle.patch
0015-network-tc-use-typesafe-functions-to-append-netlink-.patch
0016-network-tc-drop-unused-functions.patch
0017-network-tc-introduce-QDiscVTable-for-future-extendab.patch
0018-network-tc-inroduce-FQ-Fair-Queue-traffic-policing.patch
0019-network-tc-support-more-attributes-for-FQ-CoDel.patch
0020-sd-netlink-add-attributes-for-FQ.patch
0021-network-tc-add-more-settings-for-FQ.patch
0022-network-tc-introduce-codel.patch
0023-network-add-more-settings-for-CoDel.patch
0024-sd-netlink-introduce-sd_netlink_message_append_s8-an.patch
Add new TC TAPRIO and ETF Qdisc network config parser and TCA netlink properties :
0001-network-tc-introduce-ETF-Earliest-TxTime-First-Qdisc.patch
0002-sd-netlink-add-netlink-properties-of-Time-Aware-Prio.patch
0003-network-tc-introduce-Time-Aware-Priority-Shaper-TAPR.patch
For now this is for Exploratory-work purposes ONLY as it still suffers several limitations and issues preventing to stage into systemd (master) .
$ ip link set $IFACE down
$ systemctl restart systemd-networkd.service
$ ip link set dev $IFACE up
systemd services Sanity-Checks¶
The following sections assumes TSN switch connectivity is a basis. IEEE 802.1Q-2018 TSN Interoperability testing include at least one-hop Kontron PCIE-0400-TSN Network Interface Card with two TSN Endpoint devices (Device A and B).
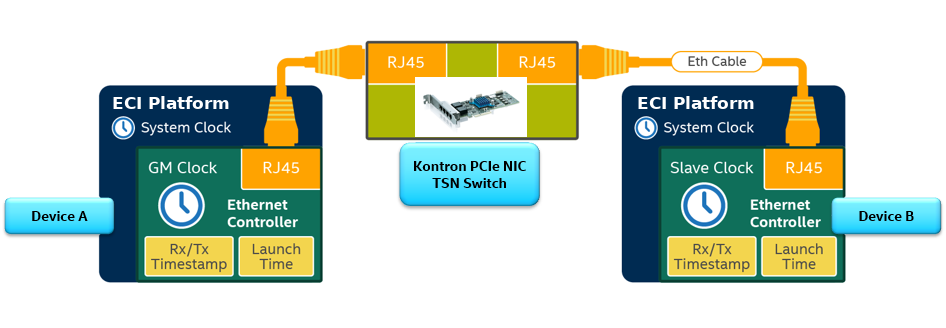
Sanity-Check #1: Set TSN Endpoint IEEE 802.1Q-2018 Gate Control List (GCL) via systemd Boot Configuration¶
This section explores how to use the systemd boot configuration provided in ECI images to automatically configure TSN parameters at boot time.
The following section is applicable to:

Step 1: Identify TSN interface name.
Perform the following command to identify the I210 interface:
/usr/sbin/lspciThe expected output appears as follows:
01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I210 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 03)The output pattern is
${device_id} ${description}, where${device_id}is01:00.0in this example.Important
There may be more than one I210 interface. Be sure to identify the interface which is wired to the switch device.
Perform the following commands to identify the I210 interface name:
ls /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:${device_id}/netThe expected output should be similar to the following:
enp1s0The output text is the interface name of i210 NIC, mark it as
${interface_name}.
Step 2: Open /boot/EFI/BOOT/grub.cfg for edit. Append the following text to the line that begins with linux /bzImage:
Note
Substitute
${interface_name}with the name of the interface identified in the previous step.Note
Substitute
${ip_address}with the desired IP address to configure the endpoint. The Sanity-Check tasks use 192.168.0.1 for${ip_address}on Device A, and 192.168.0.2 for${ip_address}on Device B.tsnep=${ip_address}/255.255.255.0,${interface_name} qdisc=TAPRIO tsn.vlan=3
Step 3: Reboot device
Step 4: Verify IP address of I210 interface.
Perform the following command:
ip address show dev ${interface_name}The expected output should be similar to the following:
4: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc taprio state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:e0:4c:98:79:19 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.0.1/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global enp1s0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverThe text
192.168.0.1in this example is the IP address assigned to the interface. Make sure this matches the value substituted earlier for${ip_address}.
Step 5: Verify vlan enabling.
Perform the following command:
ifconfig ${interface_name}.3The expected output should be similar to the following:
enp1s0.3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:E0:4C:98:79:19 inet addr:169.254.97.159 Bcast:169.254.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0 inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:4cff:fe98:7919/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING PROMISC MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:128649 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:155863 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:72269729 (68.9 MiB) TX bytes:82836724 (78.9 MiB)The first line starting with pattern
${interface_name}.3is expected.
Step 6: Verify Queue Discipline configuration
Perform the following command:
tc qdisc show dev ${interface_name}The expected output appears as follows:
qdisc taprio 100: root refcnt 9 tc 4 map 3 3 3 1 3 0 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 queues offset 0 count 1 offset 1 count 1 offset 2 count 1 offset 3 count 1 clockid TAI base-time 1579599382000000000 index 0 cmd S gatemask 0x8 interval 100000 index 1 cmd S gatemask 0x1 interval 100000 index 2 cmd S gatemask 0x2 interval 100000 index 3 cmd S gatemask 0x4 interval 200000 index 4 cmd S gatemask 0x8 interval 100000 index 5 cmd S gatemask 0x1 interval 100000 index 6 cmd S gatemask 0x2 interval 100000 index 7 cmd S gatemask 0x4 interval 200000 qdisc pfifo 0: parent 100:4 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 100:3 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 100:2 limit 1000p qdisc pfifo 0: parent 100:1 limit 1000pAll lines except line starting with ‘clockid’ are expected.
Step 7: Verify PTP Service Started.
Perform the following command:
systemctl status ptp4l@${interface_name}The expected output should be similar to the following:
● ptp4l@enp1s0.service - Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service on Interface enp1s0 Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ptp4l@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-01-21 09:35:47 UTC; 3 weeks 1 days ago Main PID: 503 (ptp4l) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915) Memory: 820.0K CGroup: /system.slice/system-ptp4l.slice/ptp4l@enp1s0.service └─503 /usr/bin/ptp4l -i enp1s0 -f /usr/lib/systemd/user/ptp4l-i210.cfg Jan 21 09:35:47 intel-rt-corei7-64 systemd[1]: Started Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service on Interface enp1s0.The text
active (running)is expected.
Step 8: Verify PHC2SYS Service Started.
Perform the following command:
systemctl status phc2sys@${interface_name}The expected output appears as follows:
● phc2sys@enp1s0.service - Synchronize system clock or PTP hardware clock (PHC) on Interface enp1s0 Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/phc2sys@.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-01-21 09:35:47 UTC; 3 weeks 1 days ago Main PID: 517 (phc2sys) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915) Memory: 472.0K CGroup: /system.slice/system-phc2sys.slice/phc2sys@enp1s0.service └─517 /usr/bin/phc2sys -s enp1s0 -O 0 -S 1.0The text
active (running)is expected.