acrn-sos¶
The following section is applicable to:

This section provides the steps to build an ECI acrn-sos (ECI-A) image.
Prerequisite
Make sure that you complete the steps in Setting up ECI Build before proceeding to build an ECI acrn-sos image.
Building ECI ``acrn-sos`` Image
The ECI acrn-sos Yocto target image provides the ACRN Hypervisor, service OS (SOS), and software utilities to manage virtual machines (VMs).
Important
ACRN is only supported on specific target platforms. For a list of platforms that support ACRN, refer to Validated Hardware Platforms. To build ACRN for non-supported platforms, refer to Compiling ACRN for different platforms.
Run the setup script:
$ ./setup.sh
A list of pre-configured use cases will be displayed. Select
customto start configuring a custom build.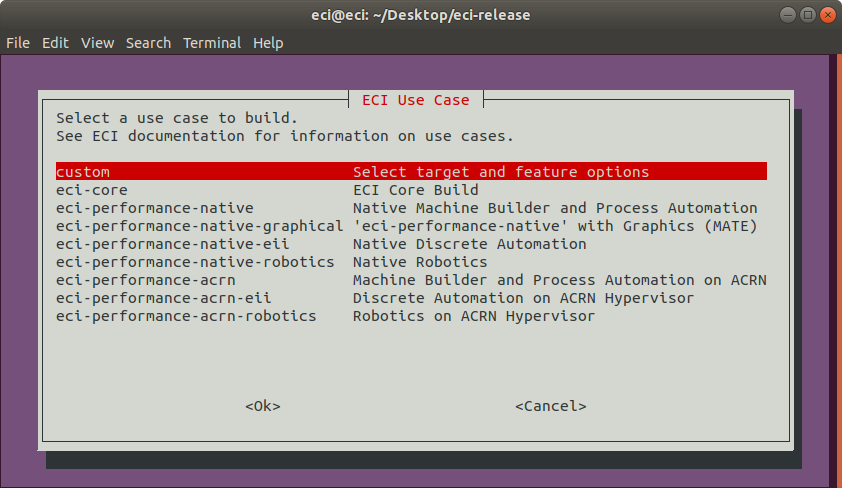
A list of available build targets will be displayed. Select
acrn-sosfrom the list.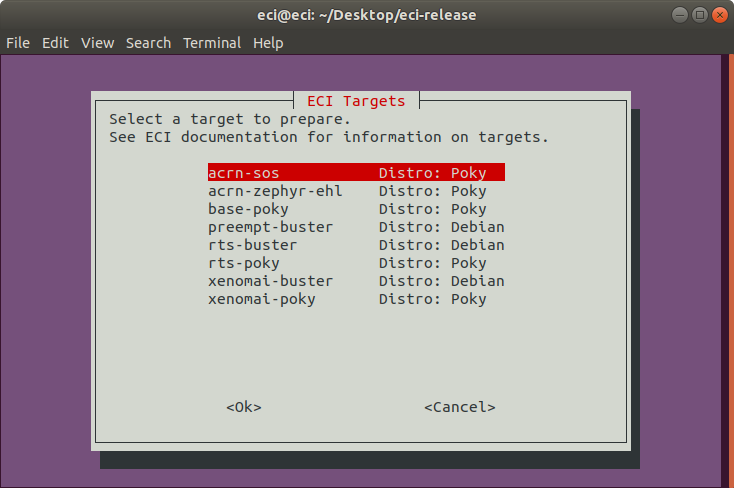
There are multiple methods to launch virtual machines (VMs) on ACRN. The table below describes the available options. Select the desired option from the list. Note: It is recommended to select
VM Launch Scriptsfor novice users of ACRN.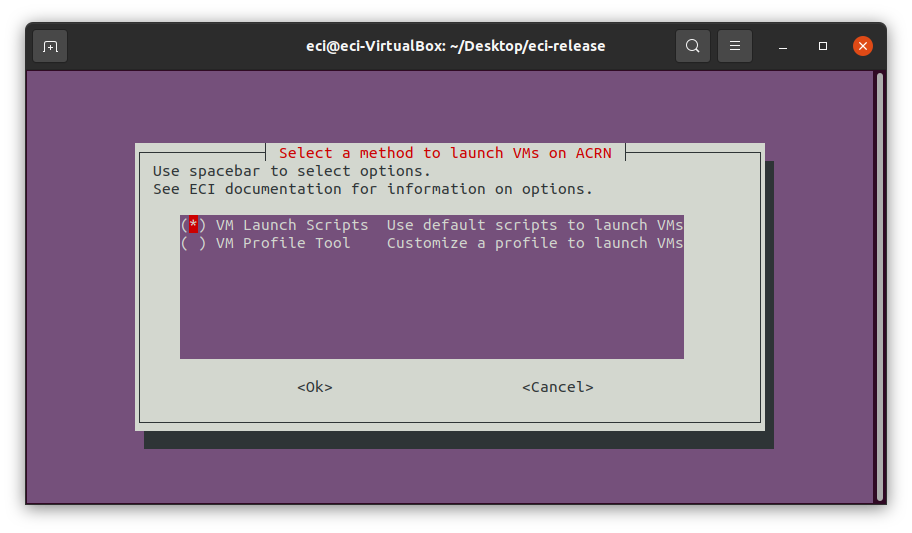
VM Launch Method
Description
VM Launch Scripts
Utilize scripts to launch VMs with generic configurations (ex: CPU, Memory). These scripts are always included in the target image. For detailed information on which launch scripts are available and what usage they are best suited for, see section VM launch scripts.
Note: This option is the simplest method and is recommended for novice users of ACRN.
VM Profile Tool
The VM Profile Tool is a menu-based interactive guide which generates a VM profile for use by automation scripts included in the target image. This tool allows a user to customize VM configurations (ex: CPU, Memory) while ensuring a valid configuration for the desired target hardware platform. For detailed information on launching VMs using the VM Profile Tool, see section VM Profile Tool.
After selecting
VM Launch Scripts, a menu will appear with the available target hardware platforms. The ACRN hypervisor is compiled based on the selected target hardware platform. On the following prompt, select the target hardware platform to compile for using the arrow keys to move the selection and spacebar to toggle the state. When complete, press the enter key to finalize the selection.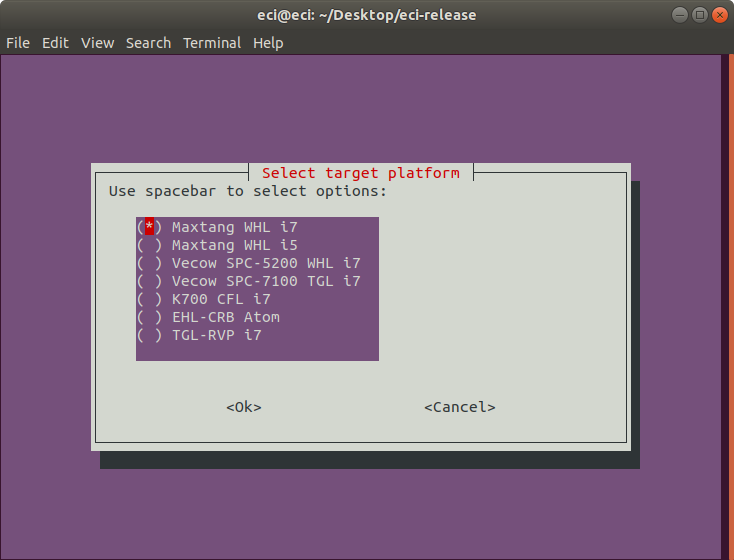
The following table lists the available options:
Target Hardware Platform
Description
Maxtang WHL i7
Maxtang WHL i5
Vecow SPC-5200 WHL i7
Vecow SPC-7100 TGL i7
K700 CFL i7
EHL-CRB Atom
Elkhart Lake Customer Reference Board
TGL-RVP i7
Tiger Lake Reference Validation Platform
On the following prompt, it is possible to modify the build configuration of the
acrn-sostarget image. Select/deselect features to be included in the image using the arrow keys to move the selection and spacebar to toggle the state. When complete, press the enter key to finalize the selection.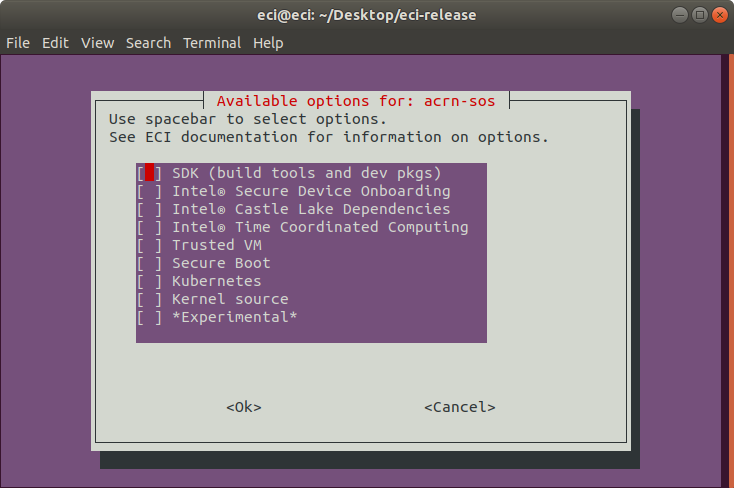
The following table lists the available options:
Feature Option
Description
SDK (build tools and dev pkgs)
Adds GCC and Make to the target image.
Intel® Castle Lake Dependencies
Adds kernel modules and tools necessary to support an Intel® Castle Lake Client.
Intel® Time Coordinated Computing
Enables Intel® Time Coordinated Computing Tools (Intel® TCC Tools) features.
Attention
Intel TCC Tools features are only supported on 11th Gen Intel® Core™ and Intel Atom® x6000E Series processors.
Trusted VM
Embed a pre-launched VM to manage TPM access.
Secure Boot
Creates a signed bootloader and boot artifacts for use with Secure Boot.
Kubernetes
Adds binaries required to join a Kubernetes cluster.
Kernel source
Adds kernel source & header files to the target image.
*Experimental*
Enables experimental features.
The setup script will begin downloading and configuring the assets needed to build the target image. Depending on the feature options selected and state of the build environment, a few notifications may occur. Some of these notifications are described below.
If the setup script is not building the target for the first time, the script will prompt:
Build directory ecs-acrn-sos already exists. Do you want to clean the cached build? y/[n]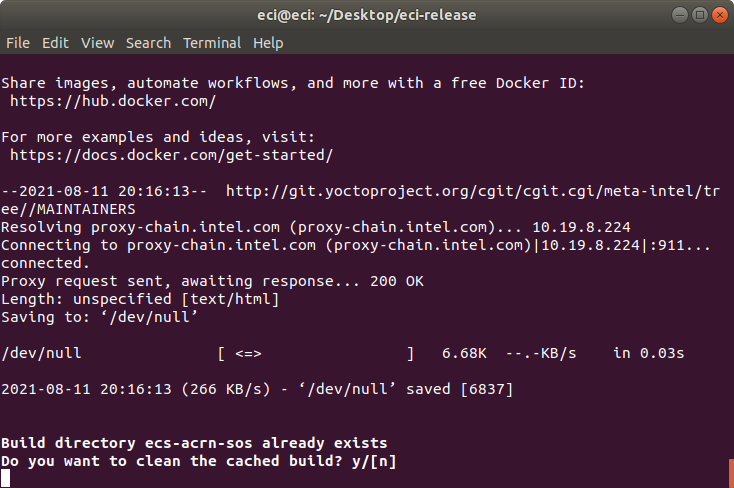
Press n to retain the target build cache, or press y to delete target build cache.
Note
It is recommended that you delete the target build cache if the target source was modified or the previous build was incomplete. Retaining the target build cache will reduce the build time, but might cause build errors if the target source was modified or the previous build was incomplete. If build errors occur, rerun the setup script and choose y at this prompt.
For all other notifications, click the following links:
After setting up the build target, a prompt will appear:
Do you want to run an automated build? y/[n]. Note: Automated builds give the option to automatically build and embed ECI images as ACRN VMs. It is recommended to perform an automated build for novice ACRN users.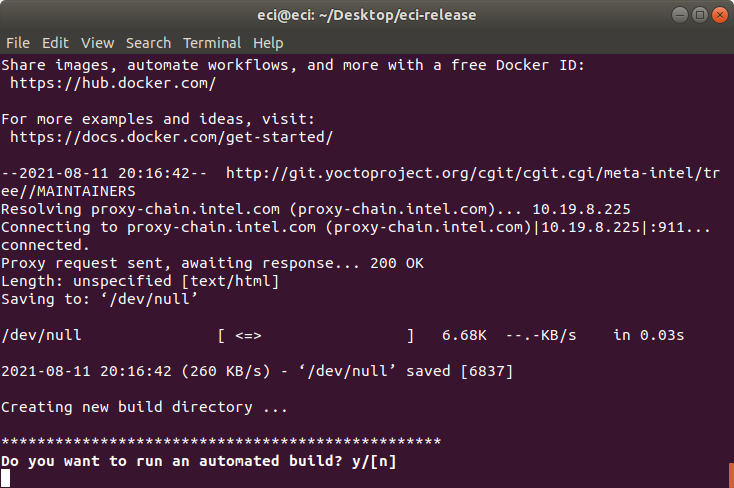
To perform an automated build, press y at the prompt.

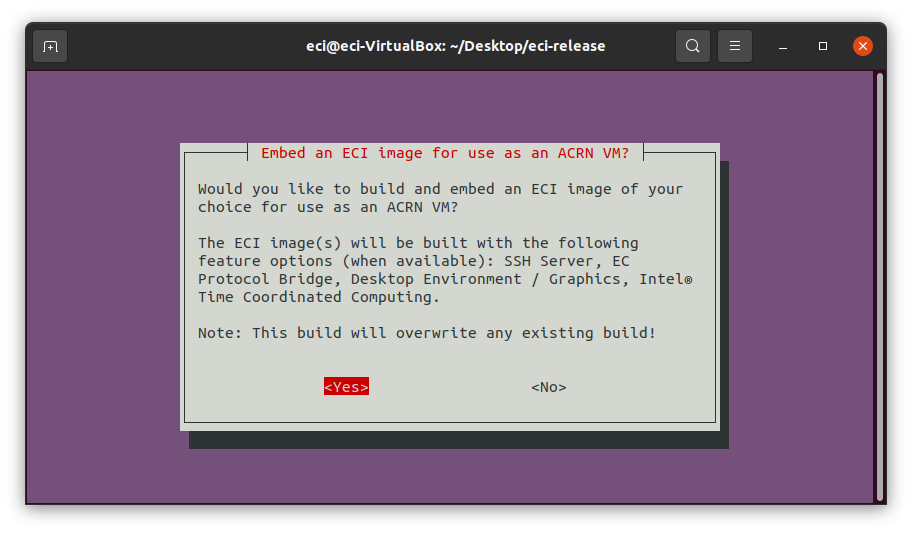
After selecting to perform an automated build, a prompt will appear asking
Embed an ECI image for use as an ACRN VM?. This prompt gives the ability to automatically build an ECI image and have it embedded into the ACRN image so that it can be launched as a VM using the VM launch scripts. To embed an ECI image as an ACRN VM, selectYesat the prompt.Note: The embedded ECI image will automatically be built with the following feature options enabled: SSH Server, EC Protocol Bridge, Desktop Environment / Graphics, and Intel® Time Coordintated Computing. This automated build will overwrite any existing build.
If
Yeswas selected to embed an ECI image, a menu will appear with the available ECI image options. Select an ECI image to build and embed as an ACRN VM.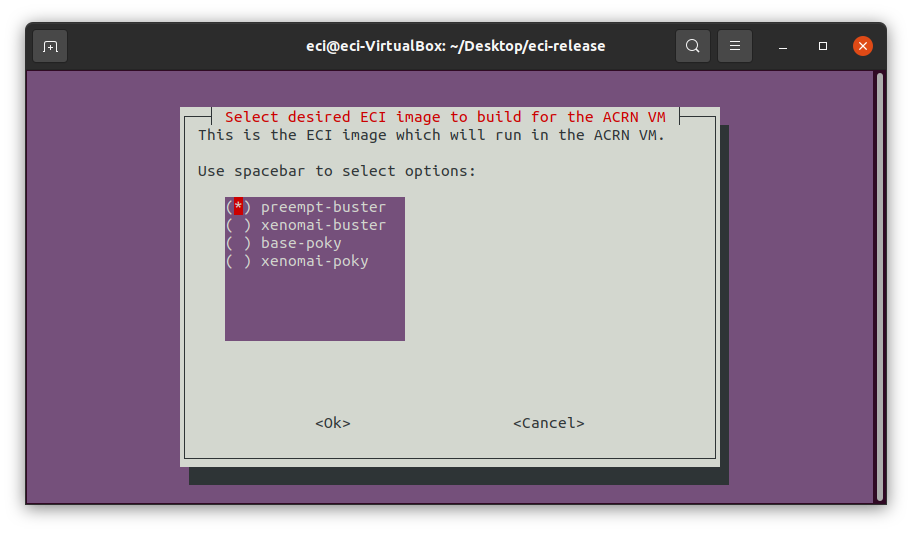
To perform a manual build, press n at the prompt. The setup script will output a completion message with the steps necessary to perform a build manually.
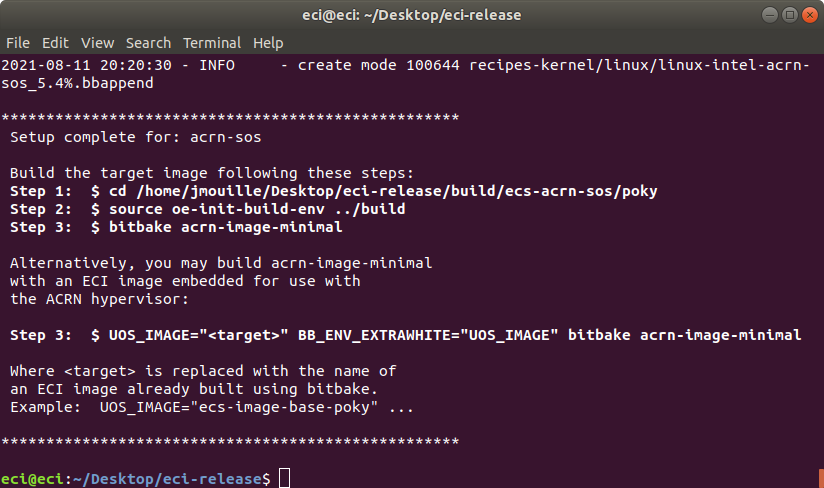
Notice that Step 3 output by the setup script has two forms:
Option A - Build an image with only the ACRN hypervisor:
$ bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Option B - Build an image with the ACRN hypervisor and embedded ECI image(s) for use as VMs:
$ UOS_TARGET="<target>" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Building Option A - ACRN hypervisor only:
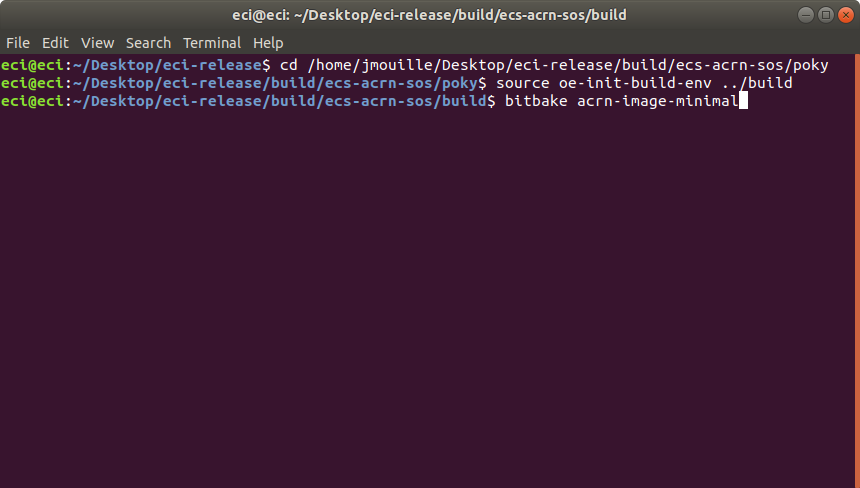
Perform the steps provided by the setup script. These steps will start the build process. For this example we performed:
$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Building Option B - ACRN hypervisor with embedded ECI image VMs:
Perform the alternative steps provided by the setup script, replacing
targetwith one or more ECI target images of choice. These steps will start the build process.Important
When specifying an ECI target name for
UOS_TARGET, the ECI target image must already be built. Specifying an ECI target which is not yet built will cause the ACRN build to fail!Note
Embedded ECI targets are copied to the ACRN image at
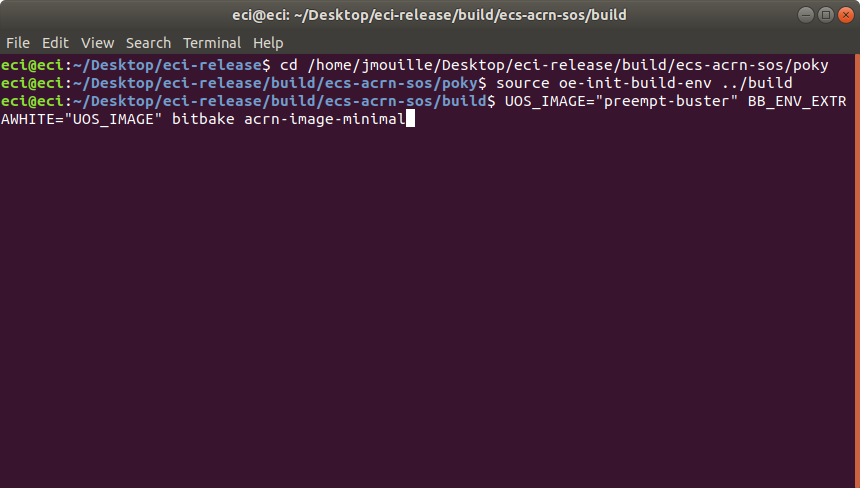
/var/lib/machines/images/vm#.wicin the order in which they are specified forUOS_TARGET. The embedded VM name will begin atvm0.wicand increment in count for each additional ECI target copied.Example 1: Embed ECI target
preempt-busterThis example will embed ECI target
preempt-busterasvm0.wicat/var/lib/machines/imagesin the ACRN image.$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ UOS_TARGET="preempt-buster" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal
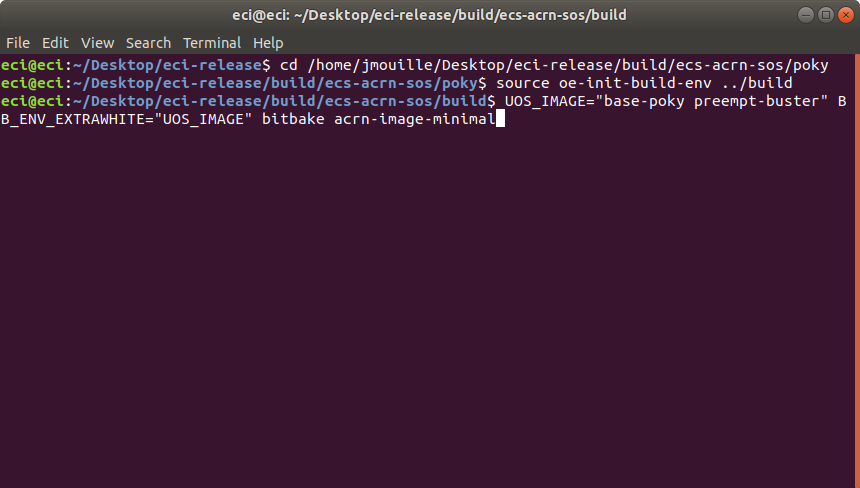
Example 2: Embed ECI targets
base-pokyandpreempt-busterThis example will embed ECI targets
base-pokyandpreempt-busterasvm0.wicandvm1.wicrespectively at/var/lib/machines/imagesin the the ACRN image.$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ UOS_TARGET="base-poky preempt-buster" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Note
The VM Profile Tool currently exposes the following configurations for ACRN VMs:
Image selection (ECI, Linux, Windows)
CPU affinity
Memory allocation
Real-time features
Graphics passthrough (GVT-D)
USB keyboard & mouse passthrough
After selecting
VM Profile Tool, a new menu guide will appear. Select an existing profile or create a new one. Selecting an existing profile will load the respective configuration. Choosing to create a new profile will start the configuration guide. For the purpose of this tutorial, we selected to create a new profile. Use the arrow keys to move the selection and press the enter key to finalize the selection. In this example, a new profile is created.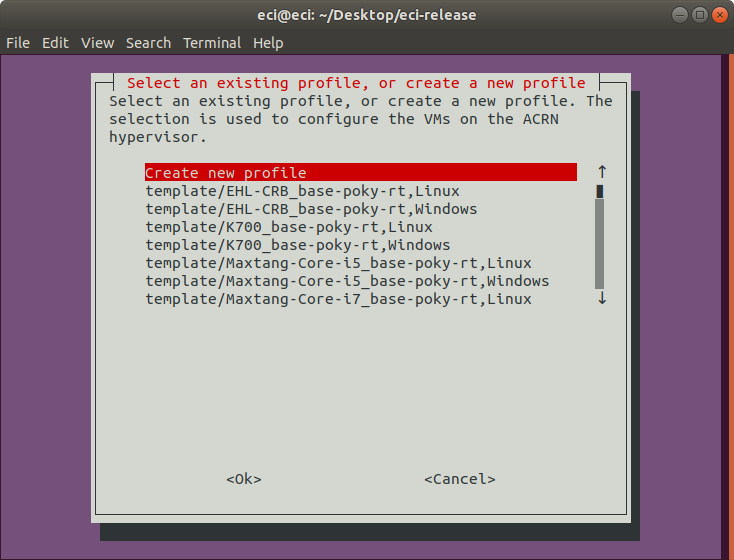
If you opted to use an existing profile, the following prompt will appear. Select the
Accept selectionoption to accept the selected profile, or selectChange selectionto return to the previous menu to make another profile selection.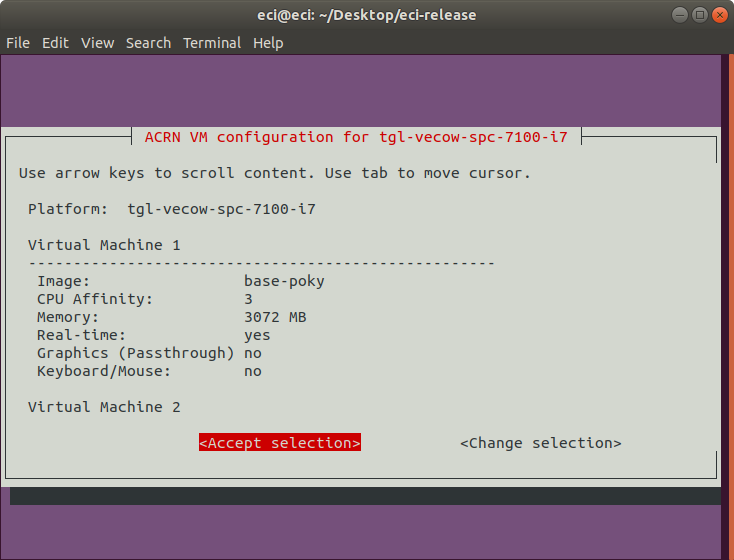
Note
If you opted to use an existing profile, skip to the remaining steps by clicking this link.
When creating a new VM profile, it is possible to start with an existing profile/template. Choosing an existing profile/template will load the respective configuration into the tool. Choosing
Default empty templatewill load a blank configuration into the tool. In this example, an existing template is selected.Important
The selected profile will determine the target hardware platform for which the
acrn-sostarget is compiled. Only the target hardware platform for which theacrn-sostarget was compiled for will correctly work with the resulting target image.Note
When choosing an existing template, select a template designed for the specific target hardware platform. Due to differences in target hardware platform capabilities, it is not possible to modify the target hardware platform of an existing template. Only the VM configuration parameters of an existing template can be modified.

The following prompt will appear if you select the
Default empty template. Select a target hardware platform that will host the ACRN hypervisor and the various VMs. Use the arrow keys to move the selection and spacebar to toggle the state. When complete, press the enter key to finalize the selection.
The following table lists the available options:
Target Hardware Platform
Description
Maxtang WHL i7
Maxtang WHL i5
Vecow SPC-5200 WHL i7
Vecow SPC-7100 TGL i7
K700 CFL i7
EHL-CRB Atom
Elkhart Lake Customer Reference Board
TGL-RVP i7
Tiger Lake Reference Validation Platform
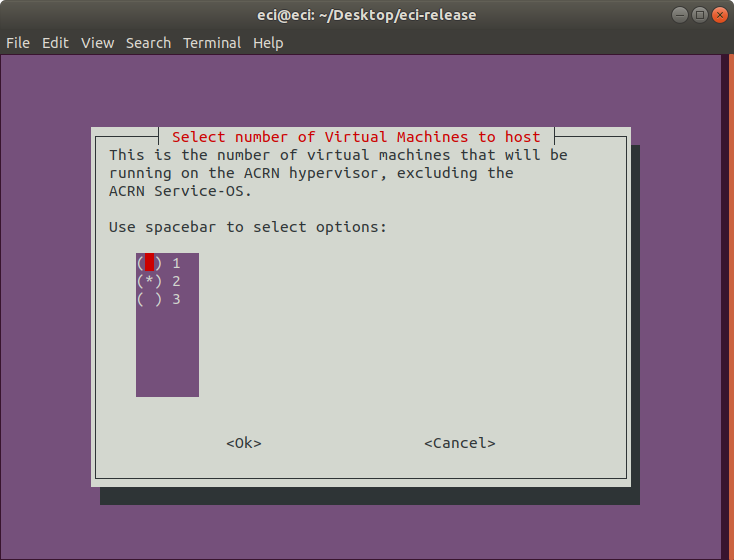
Next, select the number of VMs to host. This is the number of VMs that will be running on the ACRN hypervisor, excluding the ACRN Service-OS.
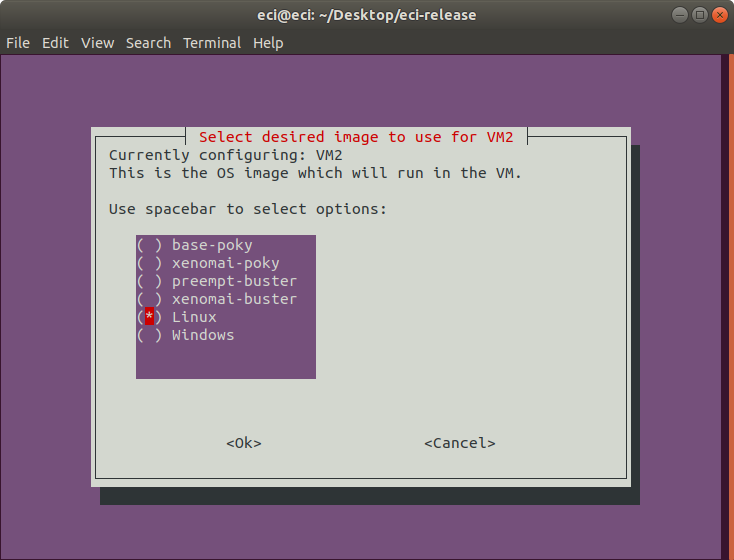
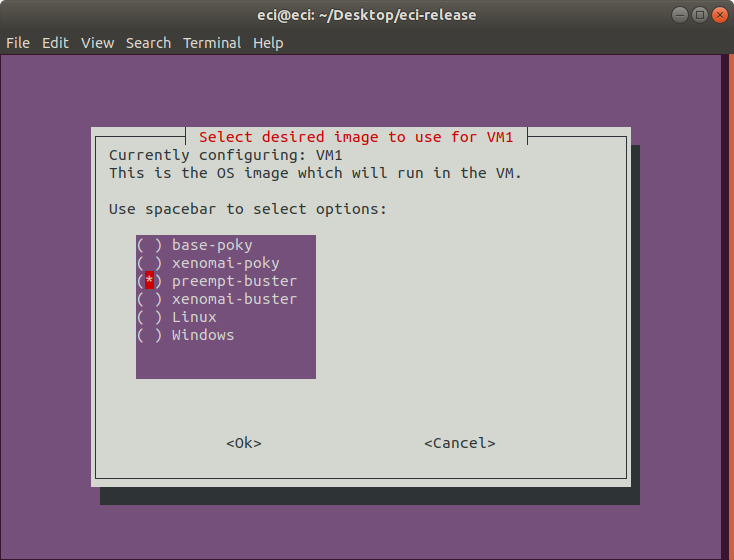
Next, select the image that you want to use for the VM. The options include ECI images, Linux, and Windows.
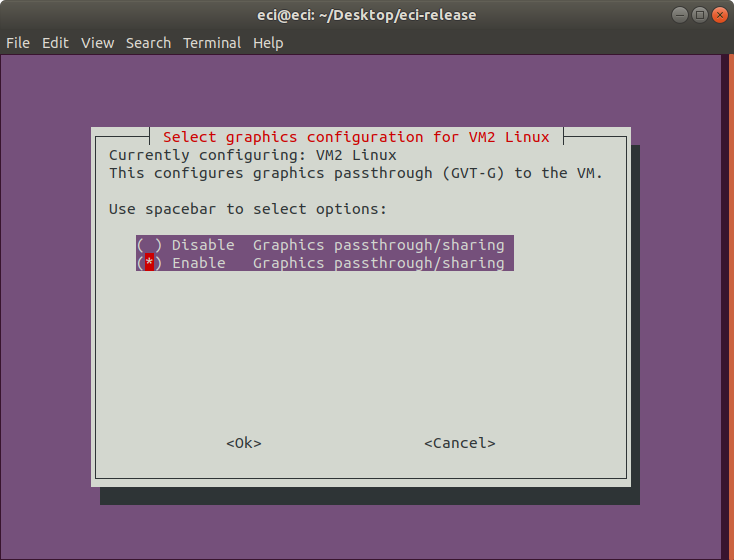
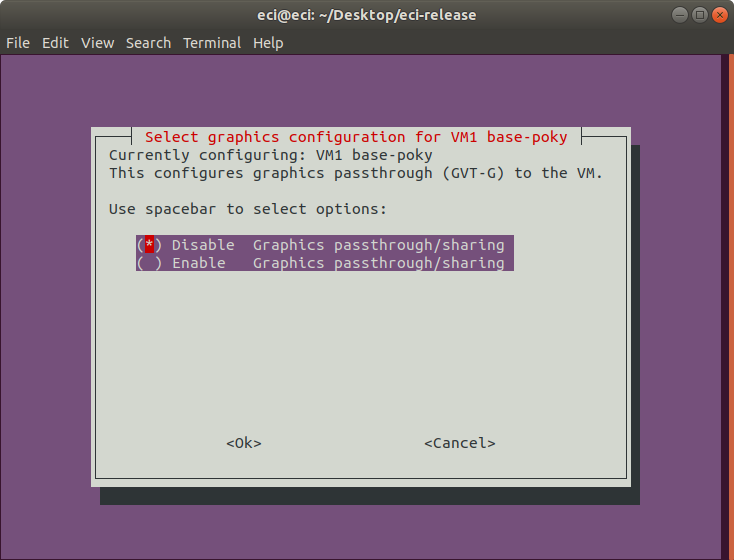
Next, select the graphics configuration for the VM. If enabled, this option will configure graphics passthrough (GTV-D) to the VM.
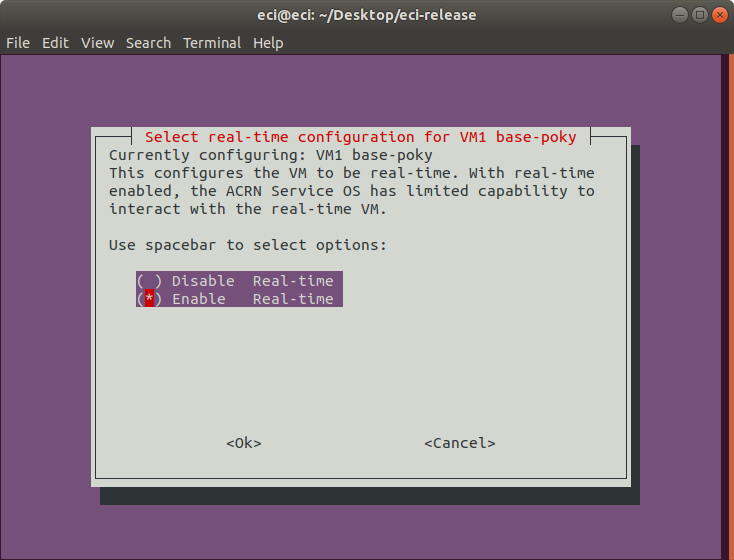
Next, select the real-time configuration for the VM. If enabled, this option will configure the VM to be real-time. With real-time enabled, the ACRN Service-OS has limited capability to interact with the real-time VM.
Important
It is only possible to configure a single VM to be real-time. If another VM has already been configured as real-time, this prompt will not appear.
Note
Some images (Windows, Linux) do not support this option, so this prompt will not appear when configuring VMs using such images.
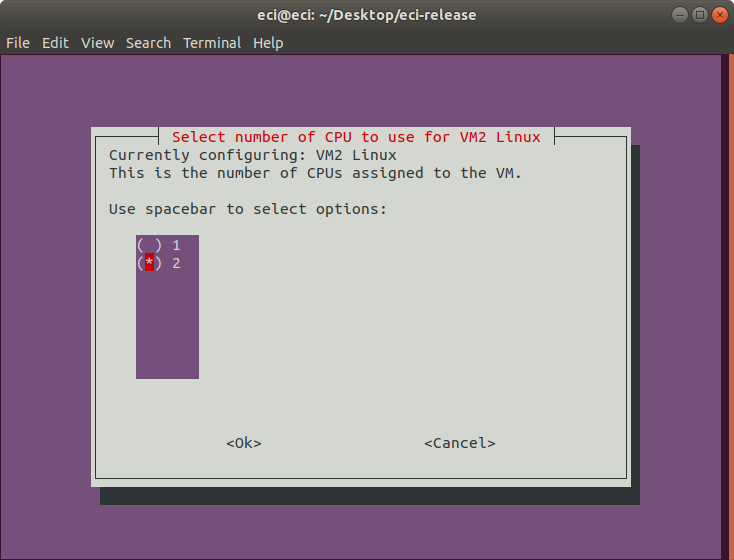
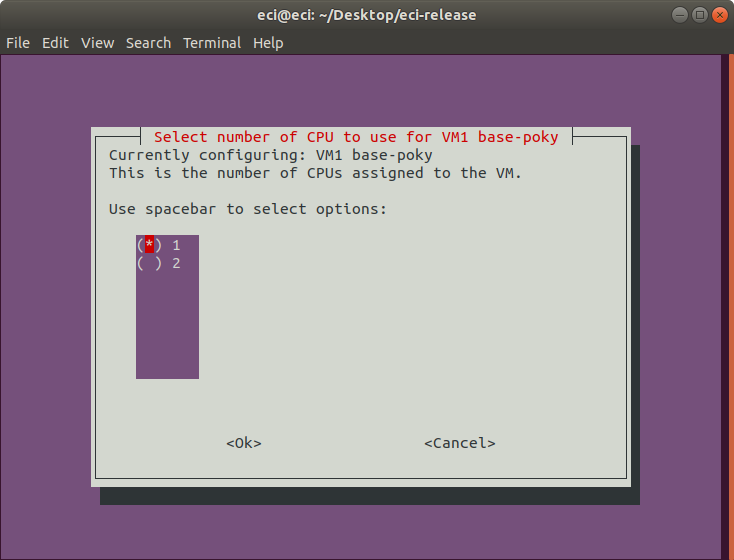
Next, select the number of CPUs to use for the VM. This selection controls the number of CPUs assigned to the VM.
Note
As CPUs are allocated to VMs, the number of available CPUs decreases. The VM Profile Tool accounts for this adjustment.
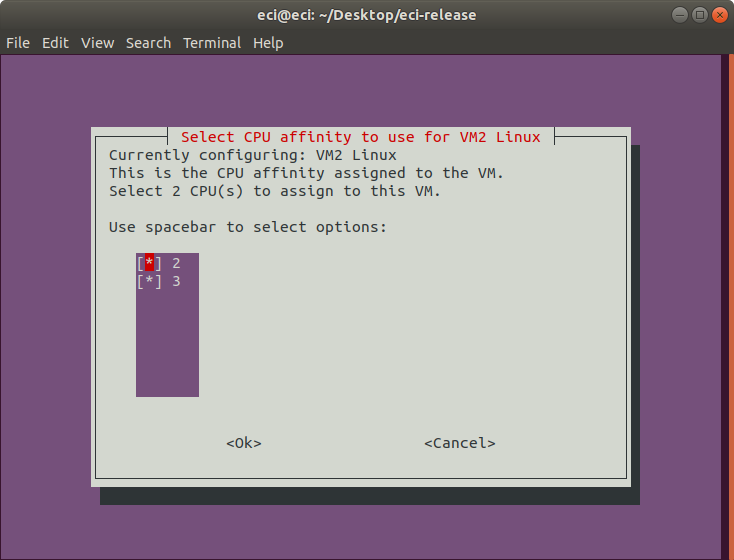
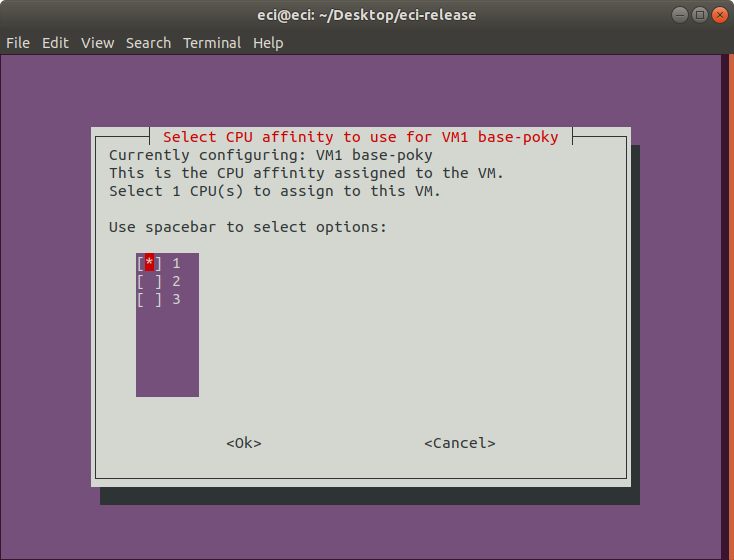
Next, select the CPU affinity to be used for the VM. This selection controls the specific CPUs assigned to the VM.
Note
It is necessary to select the same quantity of CPUs configured in the previous step. Selecting fewer or more CPUs than the previous step will display an error prompt and return to this menu.
Tip
For best real-time performance, it is recommended to assign CPU affinity such that the assigned VM CPUs reside within the same physical cores. This provides the VM exclusive access to lower level cache (L1, L2), and helps improve memory access latencies. Many processors use hyperthreading to increase the number of apparent CPUs and do so by presenting each core as two or more CPUs. As a result, CPUs are grouped in pairs based on the hyperthreading model in use. Typically, the CPU pairs that reside on the same physical core are: 0-1, 2-3, 4-5, and so on. Following this logic, selecting CPUs 2 and 3 is better than selecting CPUs 1 and 2 for a real-time VM requiring two CPUs.
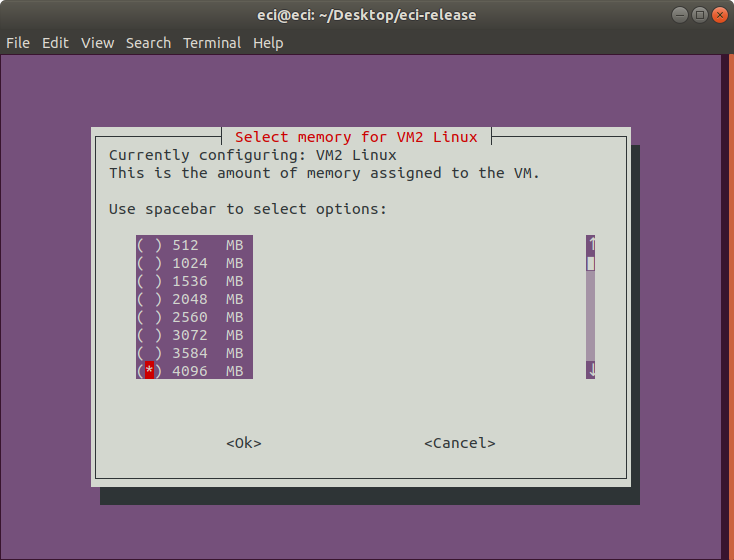
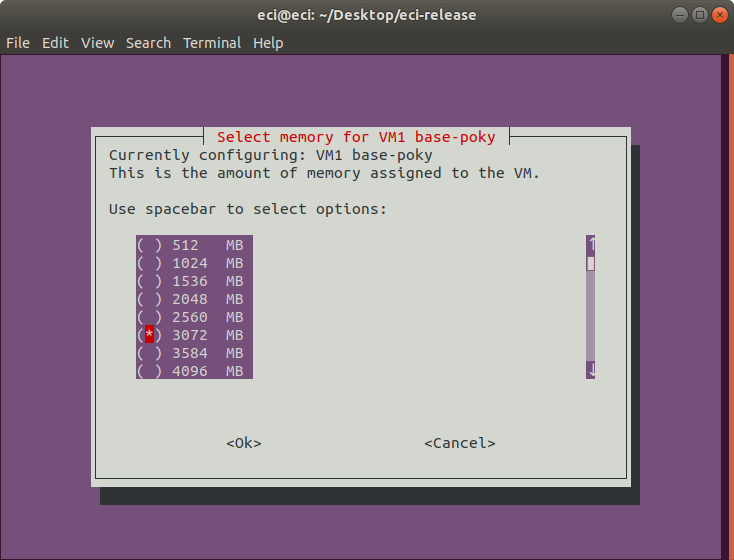
Next, select the memory to be allocated for the VM. This indicates the amount of memory that the VM will have access to.
Note
As memory is allocated to VMs, the amount of available memory decreases. The VM Profile Tool accounts for this adjustment.
At this point in the VM profile tool, the first VM has been completely configured. If there are more VMs to be configured, the VM profile tool will display the same menu prompts as explained in the previous steps. Instead of repeating the menu prompts, the images of the respective prompts are shown here:
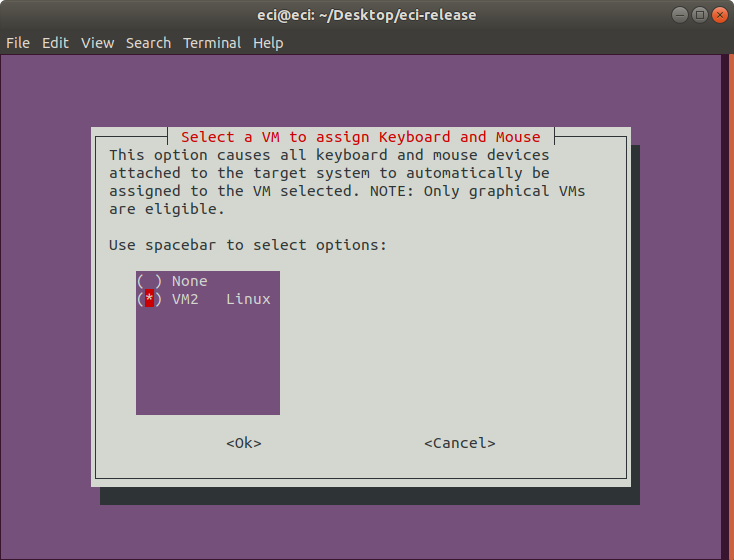
If a VM was configured with graphics enabled, the following prompt will occur. Select the graphical VM to which the keyboard and mouse will be automatically assigned.
Important
This feature does not attempt to split available keyboards and mice to multiple VMs. The mouse and keyboard can be assigned to only a single graphical VM. As a result, all keyboards and mice attached to the target hardware platform at the time of launching the VM profile will be assigned to the selected VM.
After completion of the VM configuration, a save prompt will appear. Verify the configuration parameters. If the VM configuration is correct, select
Save Configurationto continue.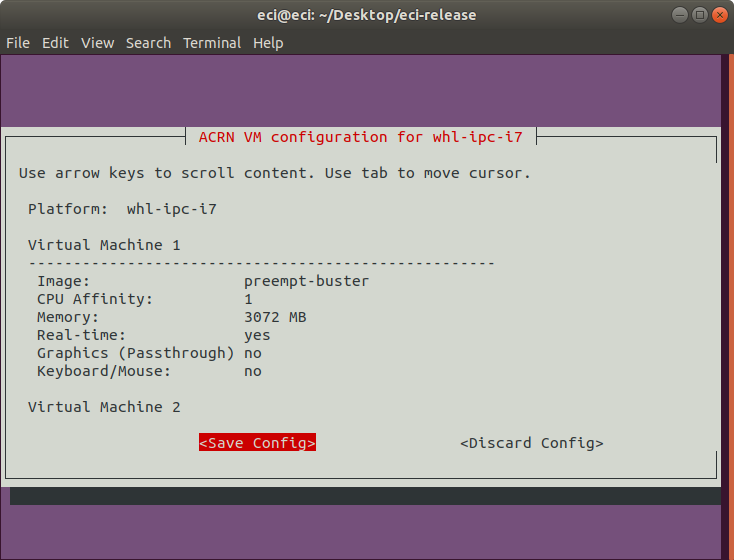
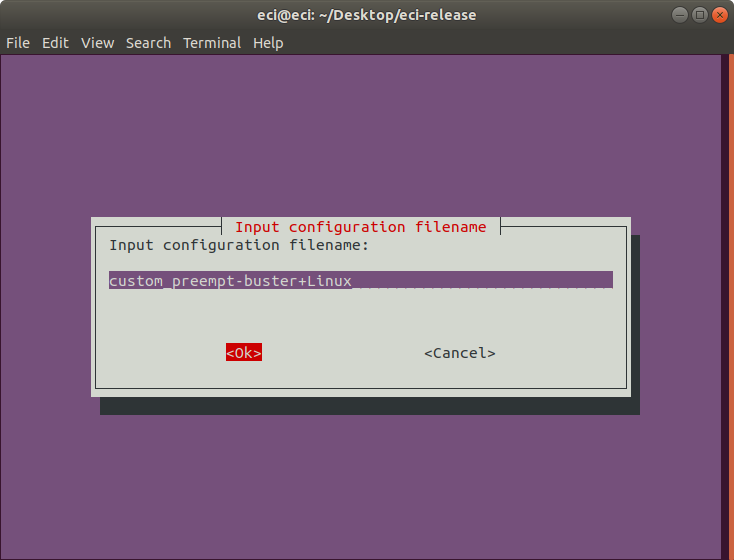
Next, enter a filename for the VM configuration.
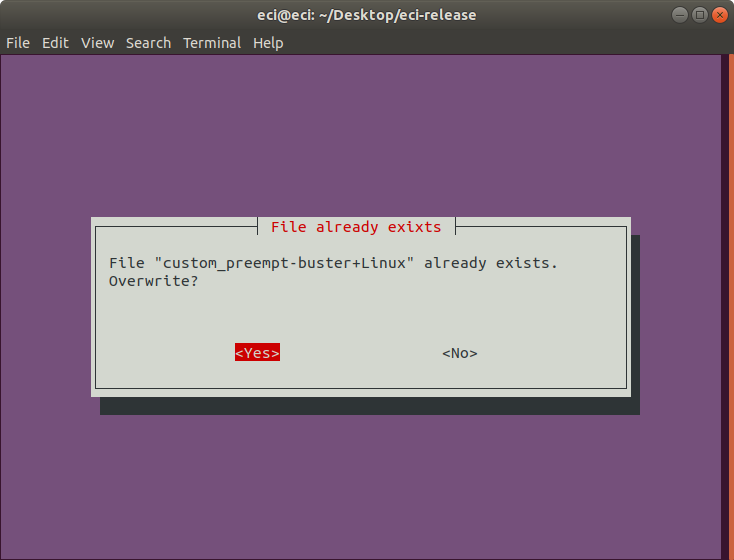
If the file already exists, a prompt will appear asking if the existing file should be overwritten:
A list of features available for
acrn-soswill be displayed. Select or deselect the features that you want to include in the image. Use the arrow keys to scroll through the list of options and use the spacebar to toggle the state. Press enter to finalize the selection.
The following table lists the available options:
Feature Option
Description
SDK (build tools and dev pkgs)
Adds GCC and Make to the target image.
Intel® Castle Lake Dependencies
Adds kernel modules and tools necessary to support an Intel® Castle Lake Client.
Intel® Time Coordinated Computing
Enables Intel® Time Coordinated Computing Tools (Intel® TCC Tools) features.
Attention
Intel TCC Tools features are only supported on 11th Gen Intel® Core™ and Intel Atom® x6000E Series processors.
Trusted VM
Embed a pre-launched VM to manage TPM access.
Secure Boot
Creates a signed bootloader and boot artifacts for use with Secure Boot.
Kubernetes
Adds binaries required to join a Kubernetes cluster.
Kernel source
Adds kernel source & header files to the target image.
*Experimental*
Enables experimental features.
The setup script will begin downloading and configuring the assets needed to build the target image. Depending on the feature options selected and state of the build environment, a few notifications may occur. Some of these notifications are described below.
If the setup script is not building the target for the first time, the script will prompt:
Build directory ecs-acrn-sos already exists. Do you want to clean the cached build? y/[n]
Press n to retain the target build cache, or press y to delete target build cache.
Note
It is recommended that you delete the target build cache if the target source was modified or the previous build was incomplete. Retaining the target build cache will reduce the build time, but might cause build errors if the target source was modified or the previous build was incomplete. If build errors occur, rerun the setup script and choose y at this prompt.
For all other notifications, click the following links:
After setting up the build target, a prompt will appear:
Do you want to run an automated build? y/[n]. Note: Automated builds give the option to automatically build ECI images selected in the VM Profile. It is recommended to perform an automated build for novice ACRN users.
To perform an automated build, press y at the prompt.

After selecting to perform an automated build, a prompt may appear asking
Build missing ECI images?. This prompt appears when the selected VM Profile includes an ECI image which is not yet built. This prompt gives the ability to automatically build the missing ECI image so that it can be used with the VM Profile Tool. To build the missing ECI image, selectYesat the prompt.Note: The missing ECI image will automatically be built with the following feature options enabled: SSH Server, EC Protocol Bridge, Desktop Environment / Graphics, and Intel® Time Coordintated Computing. This automated build will overwrite any existing build.
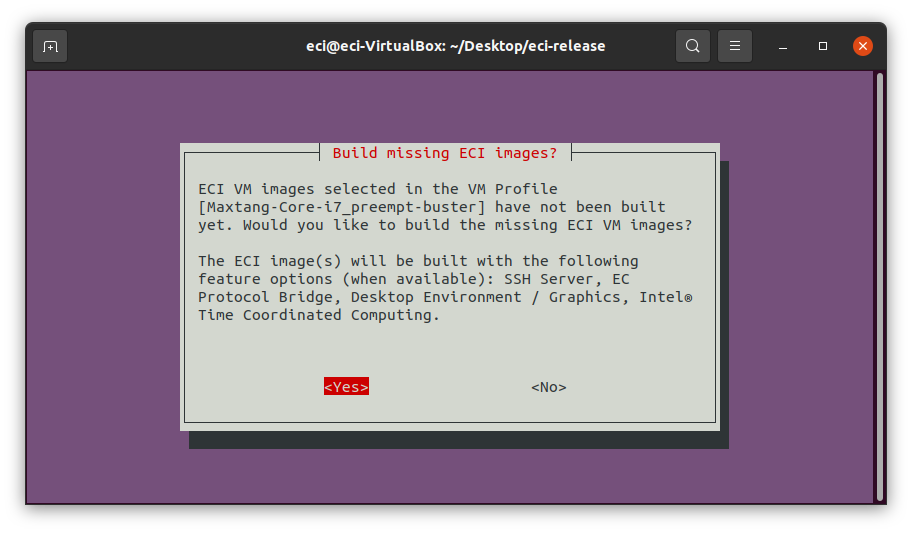
To perform a manual build, press n at the prompt. The setup script will output a completion message with the steps necessary to perform a build manually.

Notice that Step 3 output by the setup script has two forms:
Option A - Build an image with only the ACRN hypervisor:
$ bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Option B - Build an image with the ACRN hypervisor and embedded ECI image(s) for use as VMs:
$ UOS_TARGET="<target>" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal
Building Option A - ACRN hypervisor only:
Perform the steps provided by the setup script. These steps will start the build process. For this example we performed:
$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ bitbake acrn-image-minimal

Building Option B - ACRN hypervisor with embedded ECI image VMs:
Perform the alternative steps provided by the setup script, replacing
targetwith one or more ECI target images of choice. These steps will start the build process.Important
When specifying an ECI target name for
UOS_TARGET, the ECI target image must already be built. Specifying an ECI target which is not yet built will cause the ACRN build to fail!Note
Embedded ECI targets are copied to the ACRN image at
/var/lib/machines/images/vm#.wicin the order in which they are specified forUOS_TARGET. The embedded VM name will begin atvm0.wicand increment in count for each additional ECI target copied.Example 1: Embed ECI target
preempt-busterThis example will embed ECI target
preempt-busterasvm0.wicat/var/lib/machines/imagesin the ACRN image.$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ UOS_TARGET="preempt-buster" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal

Example 2: Embed ECI targets
base-pokyandpreempt-busterThis example will embed ECI targets
base-pokyandpreempt-busterasvm0.wicandvm1.wicrespectively at/var/lib/machines/imagesin the the ACRN image.$ cd /home/eci/Desktop/eci-release/build/ecs-acrn-sos/poky $ source oe-init-build-env ../build $ UOS_TARGET="base-poky preempt-buster" BB_ENV_EXTRAWHITE="UOS_TARGET" bitbake acrn-image-minimal

The build typically takes a very long time. A Linux build system with the recommended specifications might take about 1-2 hours to complete. A Linux build system with the minimum specifications might take over 6 hours to complete. Refer Linux Build System for the recommended specifications.
After the build completes, refer to Installing ECI-A to create a bootable USB flash drive to install the ECI-A image.